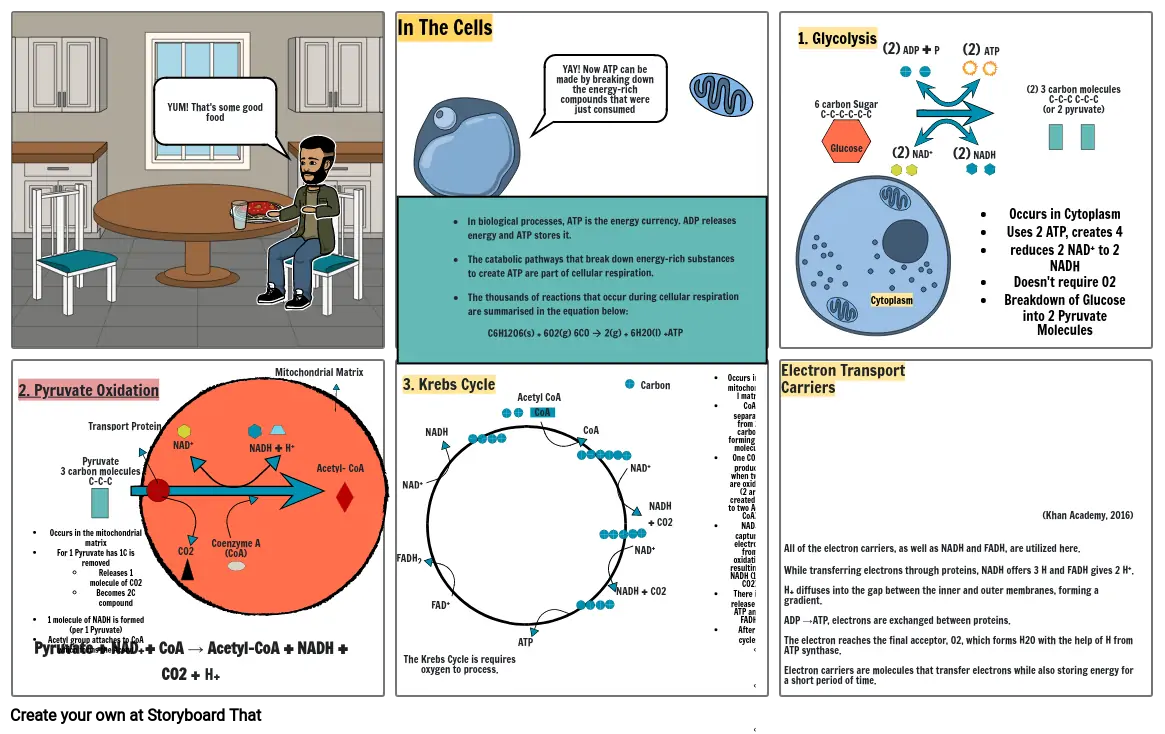
Storyboard Text
- Mitochondrial Matrix
- YUM! That's some good food
- In The Cells
- In biological processes, ATP is the energy currency. ADP releases energy and ATP stores it.The catabolic pathways that break down energy-rich substances to create ATP are part of cellular respiration.The thousands of reactions that occur during cellular respiration are summarised in the equation below:C6H12O6(s) + 6O2(g) 6CO 🡪 2(g) + 6H2O(l) +ATP
- YAY! Now ATP can be made by breaking down the energy-rich compounds that were just consumed
- 6 carbon SugarC-C-C-C-C-C
- 1. Glycolysis
- Glucose
- Cytoplasm
- (2) ADP + P
- (2) NAD+
- (2) NADH
- (2) ATP
- Occurs in CytoplasmUses 2 ATP, creates 4 reduces 2 NAD+ to 2 NADHDoesn't require O2Breakdown of Glucose into 2 Pyruvate Molecules
- (2) 3 carbon moleculesC-C-C C-C-C(or 2 pyruvate)
- 2. Pyruvate Oxidation
- Occurs in the mitochondrial matrixFor 1 Pyruvate has 1C is removedReleases 1 molecule of CO2 Becomes 2C compound1 molecule of NADH is formed (per 1 Pyruvate)Acetyl group attaches to CoA which forms the Acetyl coenzyme A
- Pyruvate + NAD++ CoA → Acetyl-CoA + NADH + CO2 + H+
- Pyruvate3 carbon moleculesC-C-C
- Transport Protein
- NAD+
-
- CO2
- Coenzyme A (CoA)
- NADH + H+
- Acetyl- CoA
- FADH2
- NADH
- FAD+
- The Krebs Cycle is requires oxygen to process.
- NAD+
- 3. Krebs Cycle
-
- ATP
- Acetyl CoA
- CoA
- CoA
- NAD+
- NADH + CO2
- NAD+
- Carbon
- NADH + CO2
- Occurs in the mitochondrial matrixCoA separates from 2-carbon, forming a 6C molecule.One CO2 is produced when two C are oxidized (2 are created due to two Acytle CoA)NAD+ captures electrons from oxidation, resulting in NADH (1 per CO2)There is a release of 1 ATP and 1 FADH.After 2 cycles:4 CO26 NADH2 FADH2 ATP
- Electron Transport Carriers
- All of the electron carriers, as well as NADH and FADH, are utilized here.While transferring electrons through proteins, NADH offers 3 H and FADH gives 2 H+.H+ diffuses into the gap between the inner and outer membranes, forming a gradient.ADP →ATP, electrons are exchanged between proteins.The electron reaches the final acceptor, O2, which forms H2O with the help of H from ATP synthase.Electron carriers are molecules that transfer electrons while also storing energy for a short period of time.
- (Khan Academy, 2016)
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created

