Unknown Story
Storyboard Text
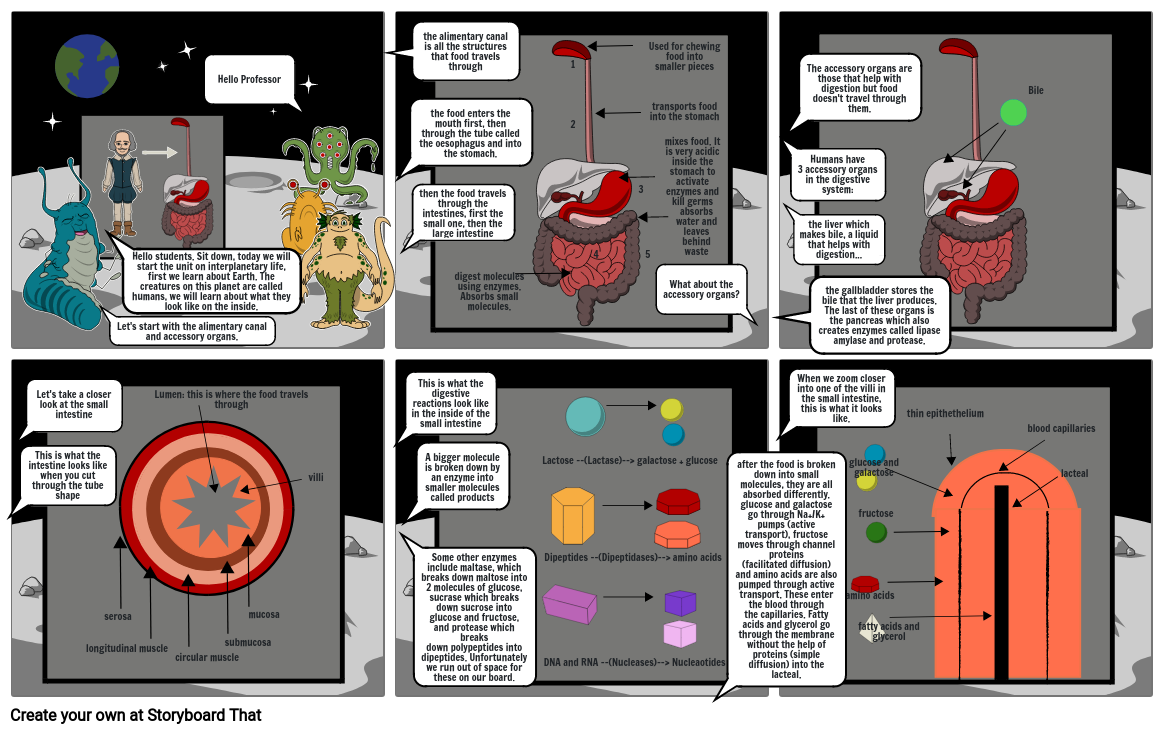
- Let's start with the alimentary canal and accessory organs.
- Hello students. Sit down, today we will start the unit on interplanetary life, first we learn about Earth. The creatures on this planet are called humans, we will learn about what they look like on the inside.
- Hello Professor
- the alimentary canal is all the structures that food travels through
- the food enters the mouth first, then through the tube called the oesophagus and into the stomach.
- then the food travels through the intestines, first the small one, then the large intestine
- digest molecules using enzymes. Absorbs small molecules.
- 12
- 4 5
- 3
- Used for chewing food into smaller piecestransports food into the stomach
- What about the accessory organs?
- mixes food. It is very acidic inside the stomach to activate enzymes and kill germs
- absorbs water and leaves behind waste
- the gallbladder stores the bile that the liver produces. The last of these organs is the pancreas which also creates enzymes called lipase amylase and protease.
- Humans have 3 accessory organs in the digestive system:
- the liver which makes bile, a liquid that helps with digestion...
- The accessory organs are those that help with digestion but food doesn't travel through them.
- Bile
- This is what the intestine looks like when you cut through the tube shape
- Let's take a closer look at the small intestine
- serosa
- longitudinal muscle
- Lumen: this is where the food travels through
- circular muscle
- submucosa
- mucosa
- villi
- This is what the digestive reactions look like in the inside of the small intestine
- Some other enzymes include maltase, which breaks down maltose into 2 molecules of glucose, sucrase which breaks down sucrose into glucose and fructose, and protease which breaks down polypeptides into dipeptides. Unfortunately we run out of space for these on our board.
- A bigger molecule is broken down by an enzyme into smaller molecules called products
- Lactose --(Lactase)--> galactose + glucose
- Dipeptides --(Dipeptidases)--> amino acids
- DNA and RNA --(Nucleases)--> Nucleaotides
- after the food is broken down into small molecules, they are all absorbed differently. glucose and galactose go through Na+/K+ pumps (active transport), fructose moves through channel proteins (facilitated diffusion) and amino acids are also pumped through active transport. These enter the blood through the capillaries. Fatty acids and glycerol go through the membrane without the help of proteins (simple diffusion) into the lacteal.
- When we zoom closer into one of the villi in the small intestine, this is what it looks like.
- amino acids
- glucose and galactose
- fructose
- fatty acids and glycerol
- thin epithethelium
- blood capillaries
- lacteal
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created

