Storyboard Text
- Once on the Mediterranean sea, was held a spectacular cruise party.
- Newton, Galileo and Aristotle met at the cruise party.
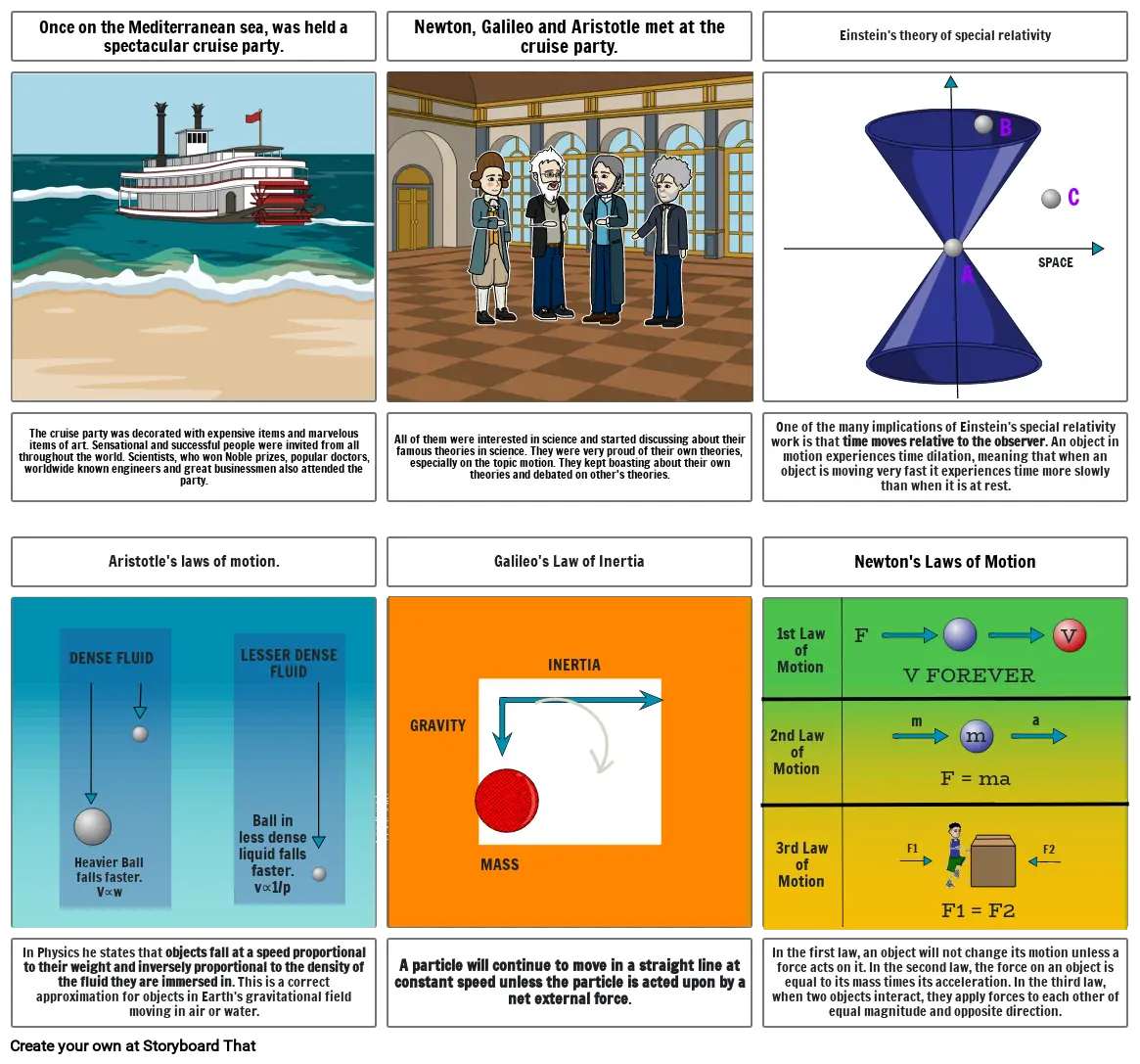
- Einstein's theory of special relativity
- A
- B
- SPACE
- C
- The cruise party was decorated with expensive items and marvelous items of art. Sensational and successful people were invited from all throughout the world. Scientists, who won Noble prizes, popular doctors, worldwide known engineers and great businessmen also attended the party.
- Aristotle's laws of motion.
- DENSE FLUID
- LESSER DENSE FLUID
- All of them were interested in science and started discussing about their famous theories in science. They were very proud of their own theories, especially on the topic motion. They kept boasting about their own theories and debated on other's theories.
- Galileo's Law of Inertia
- GRAVITY
- INERTIA
- One of the many implications of Einstein's special relativity work is that time moves relative to the observer. An object in motion experiences time dilation, meaning that when an object is moving very fast it experiences time more slowly than when it is at rest.
- Newton's Laws of Motion
- 1st Law of Motion
- F
- V FOREVER
- V
- In Physics he states that objects fall at a speed proportional to their weight and inversely proportional to the density of the fluid they are immersed in. This is a correct approximation for objects in Earth's gravitational field moving in air or water.
- Heavier Ball falls faster.V∝w
- Ball in less dense liquid falls faster.v∝1/p
- A particle will continue to move in a straight line at constant speed unless the particle is acted upon by a net external force.
- MASS
- In the first law, an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it. In the second law, the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. In the third law, when two objects interact, they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude and opposite direction.
- 2nd Law of Motion
- 3rd Law of Motion
- F1 = F2
- m
- F1
- F = ma
- m
- a
- F2
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
