Newton's Laws Project
Storyboard Description
By: Remy Laurens
Storyboard Text
- Newton's First Law of Inertia
- Newton's Second Law of Accelertation
- Newton's Third Law of Action and Reaction
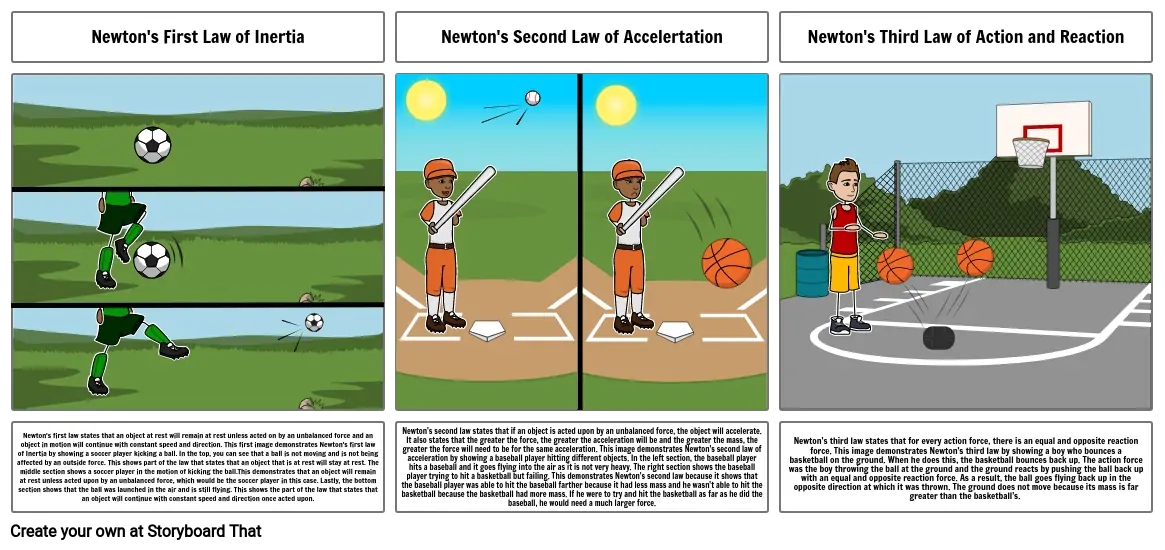
- Newton's first law states that an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an unbalanced force and an object in motion will continue with constant speed and direction. This first image demonstrates Newton's first law of Inertia by showing a soccer player kicking a ball. In the top, you can see that a ball is not moving and is not being affected by an outside force. This shows part of the law that states that an object that is at rest will stay at rest. The middle section shows a soccer player in the motion of kicking the ball.This demonstrates that an object will remain at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force, which would be the soccer player in this case. Lastly, the bottom section shows that the ball was launched in the air and is still flying. This shows the part of the law that states that an object will continue with constant speed and direction once acted upon.
- Newton's second law states that if an object is acted upon by an unbalanced force, the object will accelerate. It also states that the greater the force, the greater the acceleration will be and the greater the mass, the greater the force will need to be for the same acceleration. This image demonstrates Newton's second law of acceleration by showing a baseball player hitting different objects. In the left section, the baseball player hits a baseball and it goes flying into the air as it is not very heavy. The right section shows the baseball player trying to hit a basketball but failing. This demonstrates Newton's second law because it shows that the baseball player was able to hit the baseball farther because it had less mass and he wasn't able to hit the basketball because the basketball had more mass. If he were to try and hit the basketball as far as he did the baseball, he would need a much larger force.
- Newton's third law states that for every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. This image demonstrates Newton's third law by showing a boy who bounces a basketball on the ground. When he does this, the basketball bounces back up. The action force was the boy throwing the ball at the ground and the ground reacts by pushing the ball back up with an equal and opposite reaction force. As a result, the ball goes flying back up in the opposite direction at which it was thrown. The ground does not move because its mass is far greater than the basketball's.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
