1st Part of Cell Cycle Project
Storyboard Text
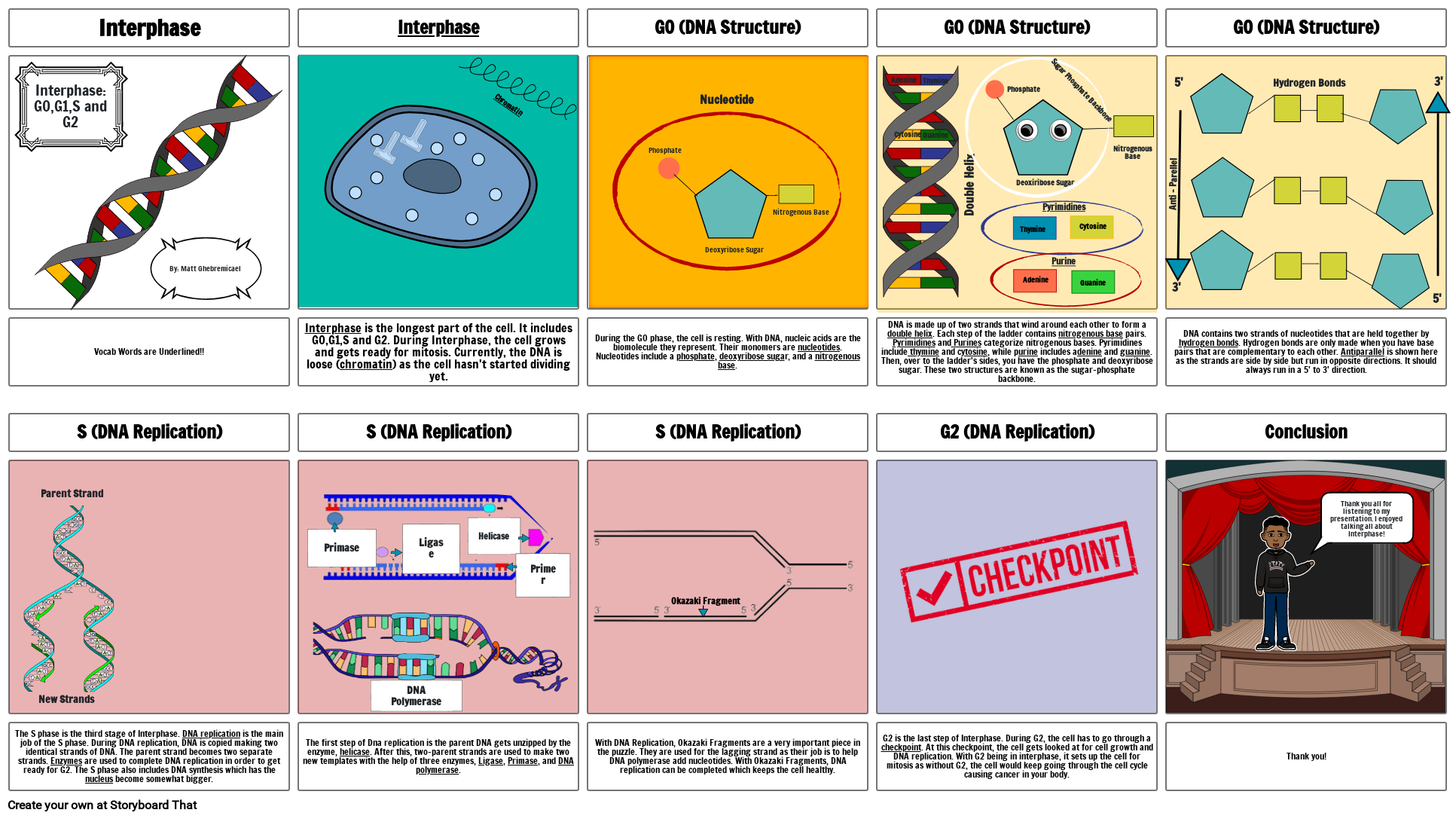
- Interphase
- Interphase: G0,G1,S and G2
- By: Matt Ghebremicael
- Interphase
- Chromatin
- G0 (DNA Structure)
- Phosphate
- Nucleotide
- Deoxyribose Sugar
- Nitrogenous Base
- Adenine
- Cytosine
- G0 (DNA Structure)
- Guanine
- Thymine
- Double Helix
- Phosphate
- Thymine
- Adenine
- Deoxiribose Sugar
- Pyrimidines
- Purine
- Sugar Phosphate Backbone
- Cytosine
- Guanine
- Nitrogenous Base
- Anti - Parellel
- 3'
- 5'
- G0 (DNA Structure)
- Hydrogen Bonds
- 3'
- Vocab Words are Underlined!!
- S (DNA Replication)
- Parent Strand
- Interphase is the longest part of the cell. It includes G0,G1,S and G2. During Interphase, the cell grows and gets ready for mitosis. Currently, the DNA is loose (chromatin) as the cell hasn't started dividing yet.
- S (DNA Replication)
- Ligase
- Helicase
- During the G0 phase, the cell is resting. With DNA, nucleic acids are the biomolecule they represent. Their monomers are nucleotides. Nucleotides include a phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base.
- S (DNA Replication)
- DNA is made up of two strands that wind around each other to form a double helix. Each step of the ladder contains nitrogenous base pairs. Pyrimidines and Purines categorize nitrogenous bases. Pyrimidines include thymine and cytosine, while purine includes adenine and guanine. Then, over to the ladder's sides, you have the phosphate and deoxyribose sugar. These two structures are known as the sugar-phosphate backbone.
- G2 (DNA Replication)
- DNA contains two strands of nucleotides that are held together by hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds are only made when you have base pairs that are complementary to each other. Antiparallel is shown here as the strands are side by side but run in opposite directions. It should always run in a 5' to 3' direction.
- Conclusion
- Thank you all for listening to my presentation. I enjoyed talking all about Interphase!
- 5'
- The S phase is the third stage of Interphase. DNA replication is the main job of the S phase. During DNA replication, DNA is copied making two identical strands of DNA. The parent strand becomes two separate strands. Enzymes are used to complete DNA replication in order to get ready for G2. The S phase also includes DNA synthesis which has the nucleus become somewhat bigger.
- New Strands
- The first step of Dna replication is the parent DNA gets unzipped by the enzyme, helicase. After this, two-parent strands are used to make two new templates with the help of three enzymes, Ligase, Primase, and DNA polymerase.
- Primase
- DNA Polymerase
- Primer
- DNA Replication
- Okazaki Fragment
- G2 is the last step of Interphase. During G2, the cell has to go through a checkpoint. At this checkpoint, the cell gets looked at for cell growth and DNA replication. With G2 being in interphase, it sets up the cell for mitosis as without G2, the cell would keep going through the cell cycle causing cancer in your body.
- Thank you!
Over 40 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
