Comic Strip
Storyboard Text
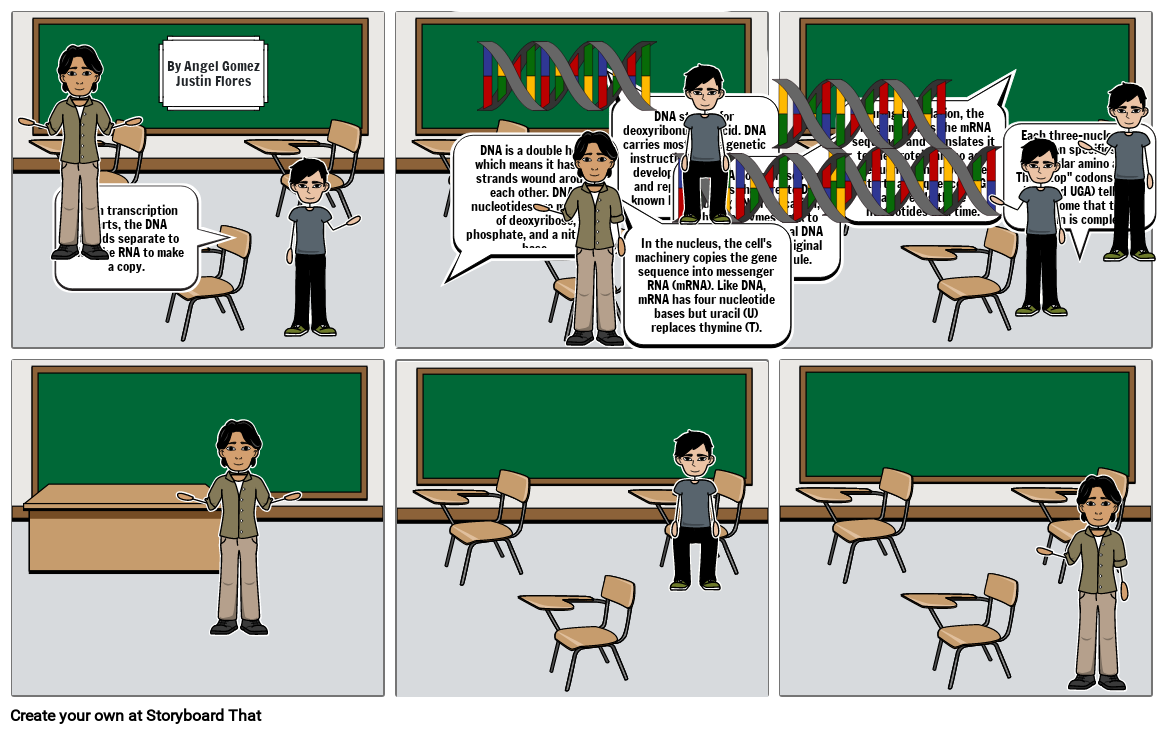
- When transcription starts, the DNA strands separate to allow the RNA to make a copy.
- By Angel Gomez Justin Flores
- DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA carries most of the genetic instructions used in the development, functioning and reproduction of all known living organisms.
- DNA is a double helix, which means it has two strands wound around each other. DNA's nucleotides are made up of deoxyribose, phosphate, and a nitrogen base.
- DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA carries most of the genetic instructions used in the development, function, and reproduction of all known living organisms.
- In the nucleus, the cell's machinery copies the gene sequence into messenger RNA (mRNA). Like DNA, mRNA has four nucleotide bases but uracil (U) replaces thymine (T).
- The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA. During DNA replication, these enzymes work to create two identical DNA strands from an original single DNA molecule.
- During translation, the ribosome reads the mRNA sequence and translates it to the protein amino acid sequence. The ribosome starts at sequence AUG and reads three nucleotides at a time.
- Each three-nucleotide codon specifies a particular amino acid. The stop codons (UAA, UAG and UGA) tell the ribosome that the protein is complete.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created

