Carbon Atom in Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Storyboard Text
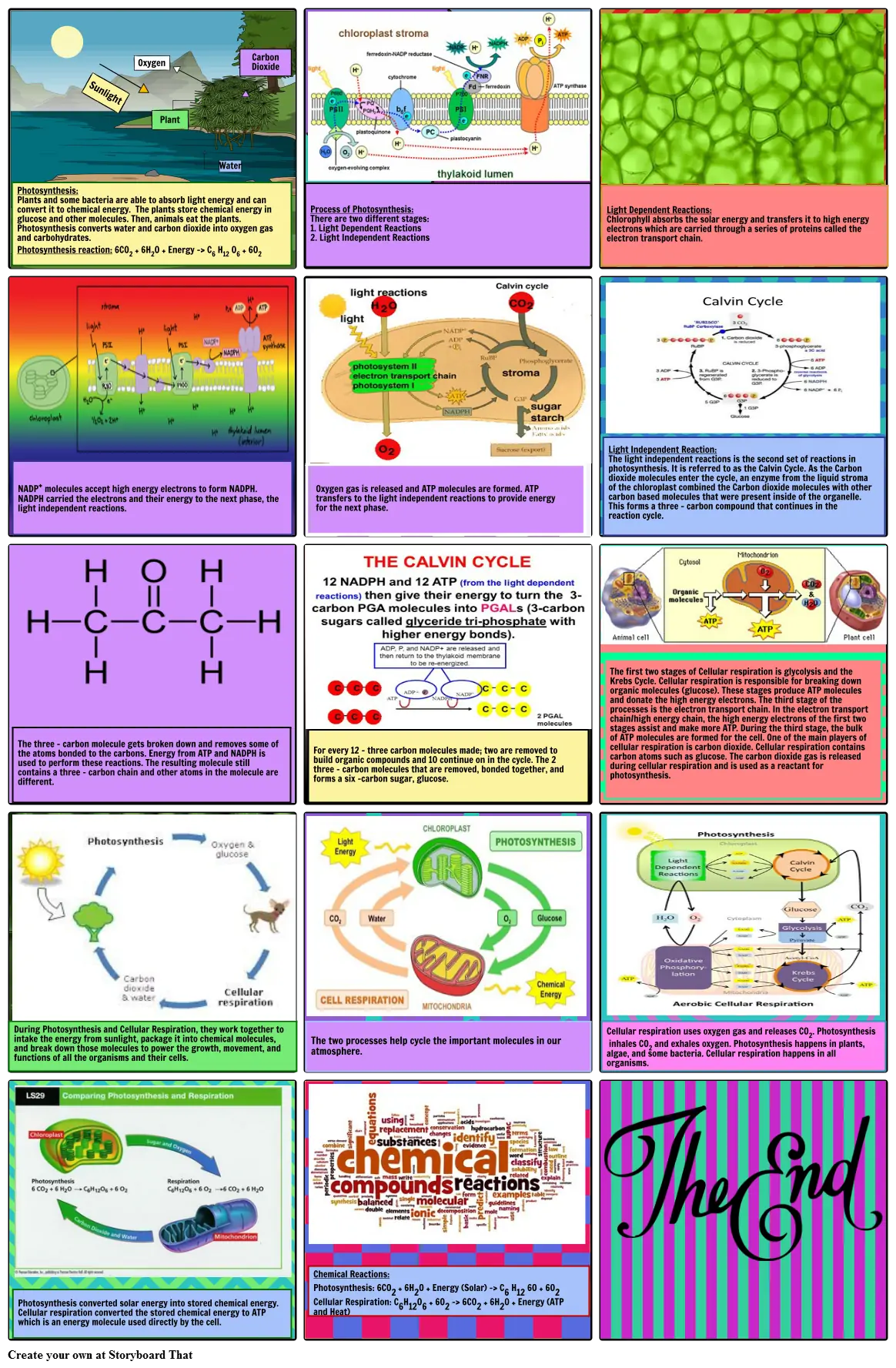
- Photosynthesis: Plants and some bacteria are able to absorb light energy and can convert it to chemical energy. The plants store chemical energy in glucose and other molecules. Then, animals eat the plants. Photosynthesis converts water and carbon dioxide into oxygen gas and carbohydrates. Photosynthesis reaction: 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy -> C6 H12 O6 + 6O2
- Sunlight
- Oxygen
- Plant
- Water
- Carbon Dioxide
- Process of Photosynthesis: There are two different stages: 1. Light Dependent Reactions 2. Light Independent Reactions
- Light Dependent Reactions: Chlorophyll absorbs the solar energy and transfers it to high energy electrons which are carried through a series of proteins called the electron transport chain.
- NADP+ molecules accept high energy electrons to form NADPH. NADPH carried the electrons and their energy to the next phase, the light independent reactions.
- Oxygen gas is released and ATP molecules are formed. ATP transfers to the light independent reactions to provide energy for the next phase.
- Light Independent Reaction: The light independent reactions is the second set of reactions in photosynthesis. It is referred to as the Calvin Cycle. As the Carbon dioxide molecules enter the cycle, an enzyme from the liquid stroma of the chloroplast combined the Carbon dioxide molecules with other carbon based molecules that were present inside of the organelle. This forms a three - carbon compound that continues in the reaction cycle.
- The three - carbon molecule gets broken down and removes some of the atoms bonded to the carbons. Energy from ATP and NADPH is used to perform these reactions. The resulting molecule still contains a three - carbon chain and other atoms in the molecule are different.
- For every 12 - three carbon molecules made; two are removed to build organic compounds and 10 continue on in the cycle. The 2 three - carbon molecules that are removed, bonded together, and forms a six -carbon sugar, glucose.
- The first two stages of Cellular respiration is glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle. Cellular respiration is responsible for breaking down organic molecules (glucose). These stages produce ATP molecules and donate the high energy electrons. The third stage of the processes is the electron transport chain. In the electron transport chain/high energy chain, the high energy electrons of the first two stages assist and make more ATP. During the third stage, the bulk of ATP molecules are formed for the cell. One of the main players of cellular respiration is carbon dioxide. Cellular respiration contains carbon atoms such as glucose. The carbon dioxide gas is released during cellular respiration and is used as a reactant for photosynthesis.
- During Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration, they work together to intake the energy from sunlight, package it into chemical molecules, and break down those molecules to power the growth, movement, and functions of all the organisms and their cells.
- The two processes help cycle the important molecules in our atmosphere.
- Cellular respiration uses oxygen gas and releases CO2. Photosynthesis inhales CO2 and exhales oxygen. Photosynthesis happens in plants, algae, and some bacteria. Cellular respiration happens in all organisms.
- Photosynthesis converted solar energy into stored chemical energy. Cellular respiration converted the stored chemical energy to ATP which is an energy molecule used directly by the cell.
- Chemical Reactions: Photosynthesis: 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (Solar) -> C6 H12 6O + 6O2 Cellular Respiration: C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H20 + Energy (ATP and Heat)
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
