sed403
Storyboard Text
- Oxygen Oxygen Oxygen
- 2 FADH2
- 2 Pyruvate
- Glucose
- Cellular Respiration
- 2 Acetyl-CoA
- 2 NADH
- 8 NADH
- O2
- Mitochondrion Matrix
- Cytoplasm
- Mitochondrion Inner Membrane
- CO2
- Energy
- H2O
- Three Steps
- Step 1: GlycolysisStep 2: Krebs CycleStep 3: Electron Transport Chain
- Glycolysis
- 2 ATP
- 1 Glucose
- 4 (2) ATP
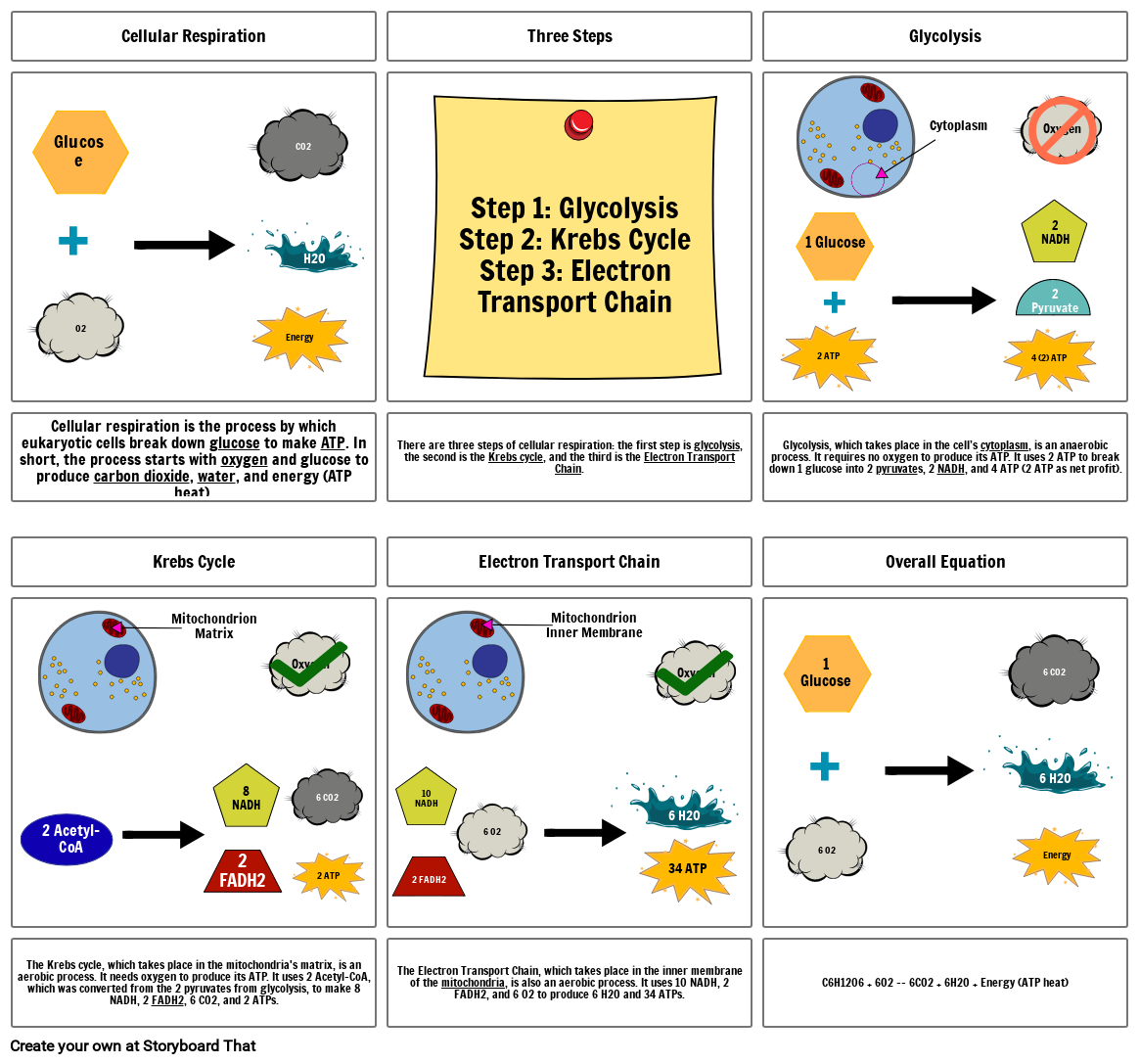
- Cellular respiration is the process by which eukaryotic cells break down glucose to make ATP. In short, the process starts with oxygen and glucose to produce carbon dioxide, water, and energy (ATP heat).
- Krebs Cycle
- There are three steps of cellular respiration: the first step is glycolysis, the second is the Krebs cycle, and the third is the Electron Transport Chain.
- Electron Transport Chain
- Glycolysis, which takes place in the cell’s cytoplasm, is an anaerobic process. It requires no oxygen to produce its ATP. It uses 2 ATP to break down 1 glucose into 2 pyruvates, 2 NADH, and 4 ATP (2 ATP as net profit).
- Overall Equation
- 1 Glucose
- 6 CO2
- The Krebs cycle, which takes place in the mitochondria's matrix, is an aerobic process. It needs oxygen to produce its ATP. It uses 2 Acetyl-CoA, which was converted from the 2 pyruvates from glycolysis, to make 8 NADH, 2 FADH2, 6 CO2, and 2 ATPs.
- 6 CO2
- 2 ATP
- The Electron Transport Chain, which takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria, is also an aerobic process. It uses 10 NADH, 2 FADH2, and 6 O2 to produce 6 H2O and 34 ATPs.
- 2 FADH2
- 10 NADH
- 6 O2
- 34 ATP
- 6 H2O
- C6H1206 + 6O2 -- 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy (ATP heat)
- 6 O2
- Energy
- 6 H2O
Over 40 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
