Bio Project
Storyboard Text
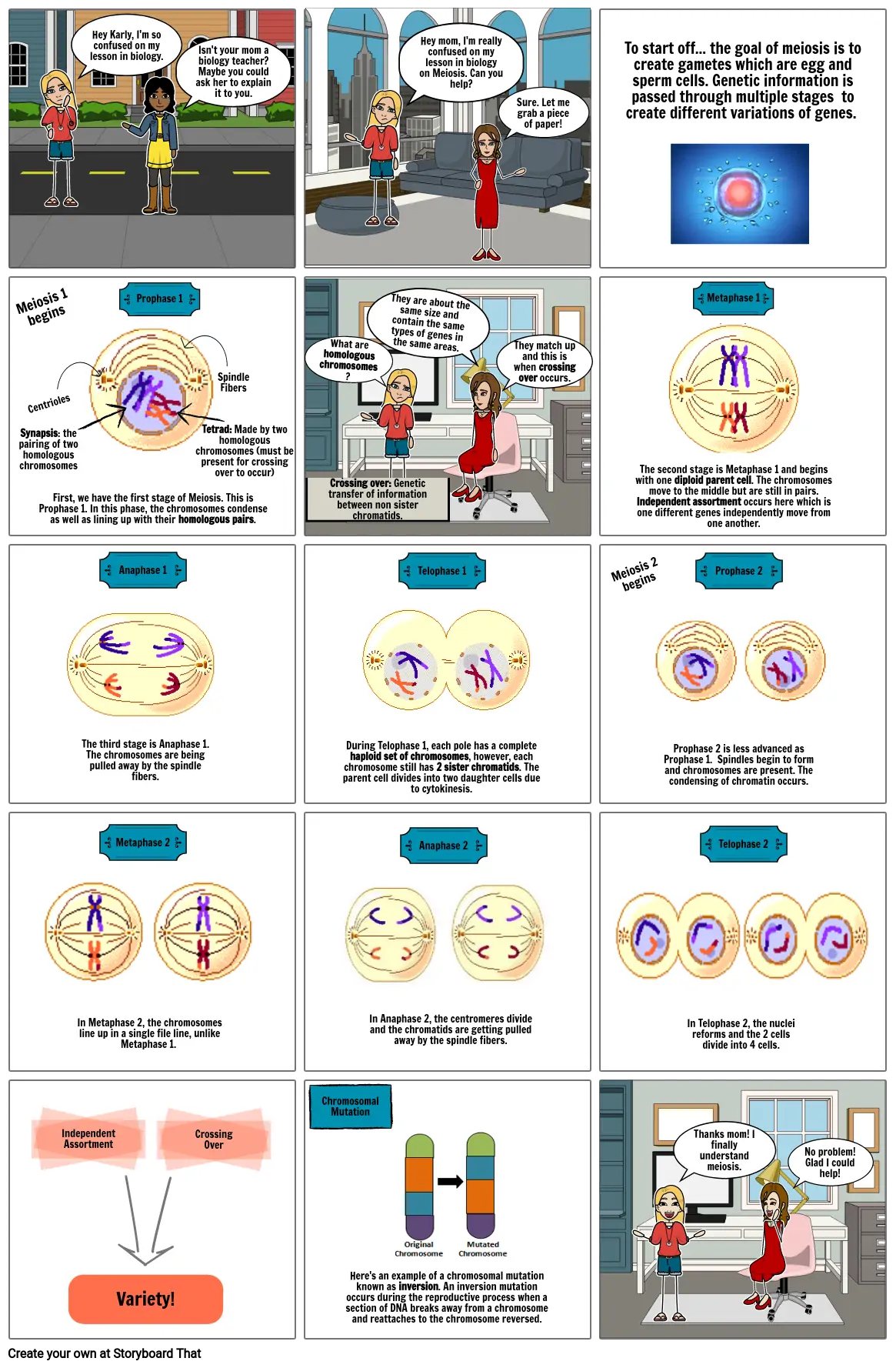
- Hey Karly, I'm so confused on my lesson in biology.
- Isn't your mom a biology teacher? Maybe you could ask her to explain it to you.
- Hey mom, I'm really confused on my lesson in biology on Meiosis. Can you help?
- Sure. Let me grab a piece of paper!
- To start off... the goal of meiosis is to create gametes which are egg and sperm cells. Genetic information is passed through multiple stages to create different variations of genes.
- Synapsis: the pairing of two homologous chromosomes
- Meiosis 1 begins
- Centrioles
- First, we have the first stage of Meiosis. This is Prophase 1. In this phase, the chromosomes condense as well as lining up with their homologous pairs.
- Prophase 1
- Tetrad: Made by two homologous chromosomes (must be present for crossing over to occur)
- SpindleFibers
- What are homologous chromosomes?
- Crossing over: Genetic transfer of information between non sister chromatids.
- They are about the same size and contain the same types of genes in the same areas.
- They match up and this is when crossing over occurs.
- The second stage is Metaphase 1 and begins with one diploid parent cell. The chromosomes move to the middle but are still in pairs. Independent assortment occurs here which is one different genes independently move from one another.
- Metaphase 1
- The third stage is Anaphase 1. The chromosomes are being pulled away by the spindle fibers.
- Anaphase 1
- During Telophase 1, each pole has a complete haploid set of chromosomes, however, each chromosome still has 2 sister chromatids. The parent cell divides into two daughter cells due to cytokinesis.
- Telophase 1
- Meiosis 2 begins
- Prophase 2 is less advanced as Prophase 1. Spindles begin to form and chromosomes are present. The condensing of chromatin occurs.
- Prophase 2
- In Metaphase 2, the chromosomes line up in a single file line, unlike Metaphase 1.
- Metaphase 2
- In Anaphase 2, the centromeres divide and the chromatids are getting pulled away by the spindle fibers.
- Anaphase 2
- In Telophase 2, the nuclei reforms and the 2 cells divide into 4 cells.
- Telophase 2
- Independent Assortment
- Variety!
- CrossingOver
- Chromosomal Mutation
- Here's an example of a chromosomal mutation known as inversion. An inversion mutation occurs during the reproductive process when a section of DNA breaks away from a chromosome and reattaches to the chromosome reversed.
- Thanks mom! I finally understand meiosis.
- No problem! Glad I could help!
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
