Informational Text storyboard
Storyboard Text
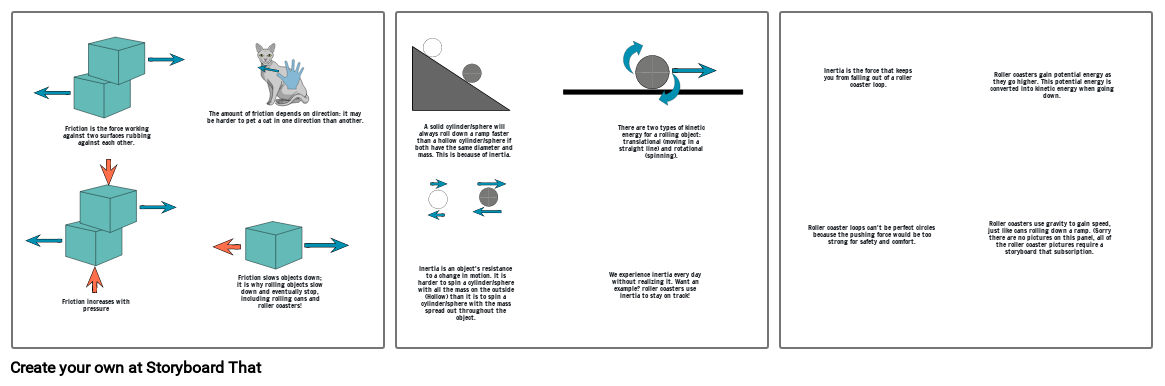
- Friction increases with pressure
- Friction is the force working against two surfaces rubbing against each other.
- The amount of friction depends on direction: it may be harder to pet a cat in one direction than another.
- Friction slows objects down; it is why rolling objects slow down and eventually stop, including rolling cans and roller coasters!
- A solid cylinder/sphere will always roll down a ramp faster than a hollow cylinder/sphere if both have the same diameter and mass. This is because of inertia.
- Inertia is an object's resistance to a change in motion. It is harder to spin a cylinder/sphere with all the mass on the outside (Hollow) than it is to spin a cylinder/sphere with the mass spread out throughout the object.
- We experience inertia every day without realizing it. Want an example? roller coasters use inertia to stay on track!
- There are two types of kinetic energy for a rolling object: translational (moving in a straight line) and rotational (spinning).
- Roller coaster loops can't be perfect circles because the pushing force would be too strong for safety and comfort.
- Inertia is the force that keeps you from falling out of a roller coaster loop.
- Roller coasters use gravity to gain speed, just like cans rolling down a ramp. (Sorry there are no pictures on this panel, all of the roller coaster pictures require a storyboard that subscription.
- Roller coasters gain potential energy as they go higher. This potential energy is converted into kinetic energy when going down.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
