Storyboard
Storyboard Text
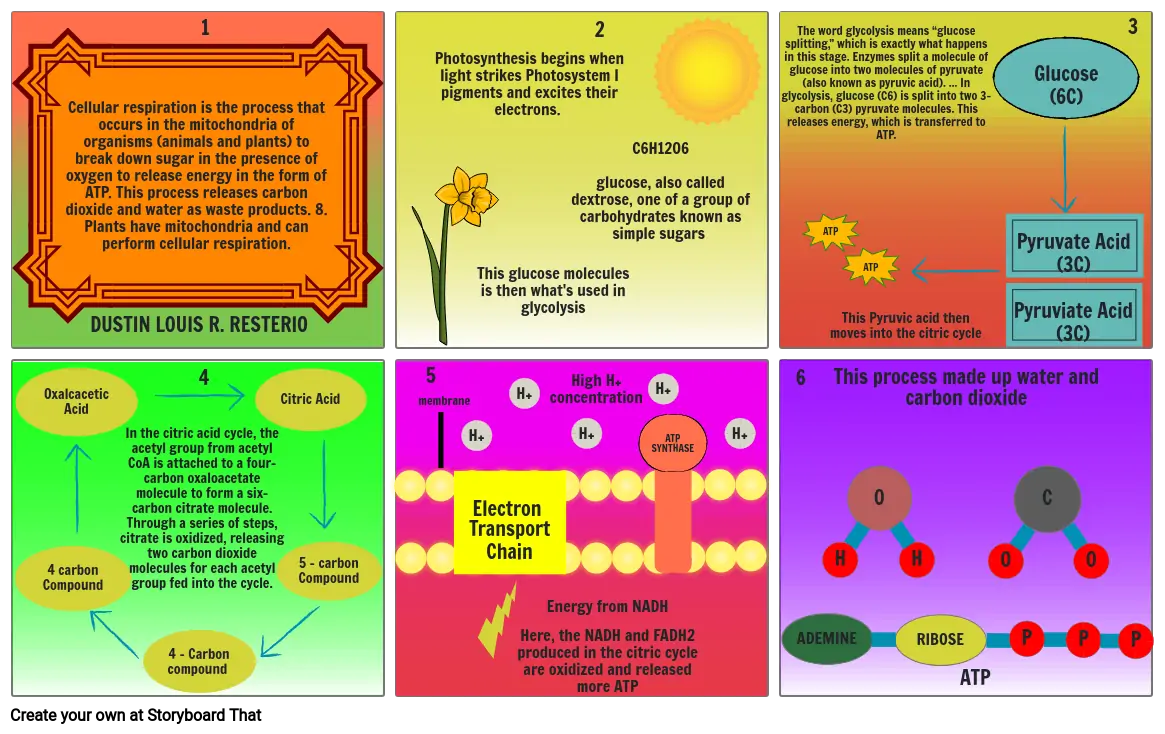
- Cellular respiration is the process that occurs in the mitochondria of organisms (animals and plants) to break down sugar in the presence of oxygen to release energy in the form of ATP. This process releases carbon dioxide and water as waste products. 8. Plants have mitochondria and can perform cellular respiration.
- DUSTIN LOUIS R. RESTERIO
- 1
- Photosynthesis begins when light strikes Photosystem I pigments and excites their electrons.
- This glucose molecules is then what's used in glycolysis
- High H+ concentration
- C6H12O6glucose, also called dextrose, one of a group of carbohydrates known as simple sugars
- 2
- The word glycolysis means “glucose splitting,” which is exactly what happens in this stage. Enzymes split a molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate (also known as pyruvic acid). ... In glycolysis, glucose (C6) is split into two 3-carbon (C3) pyruvate molecules. This releases energy, which is transferred to ATP.
- ATP
- This Pyruvic acid then moves into the citric cycle
- ATP
- Glucose(6C)
- Pyruvate Acid(3C)
- Pyruviate Acid(3C)
- 3
- 4 carbon Compound
- Oxalcacetic Acid
- In the citric acid cycle, the acetyl group from acetyl CoA is attached to a four-carbon oxaloacetate molecule to form a six-carbon citrate molecule. Through a series of steps, citrate is oxidized, releasing two carbon dioxide molecules for each acetyl group fed into the cycle.
- 4 - Carbon compound
- 4
- Citric Acid
- 5 - carbon Compound
- membrane
- 5
- Electron TransportChain
- H+
- Energy from NADHHere, the NADH and FADH2 produced in the citric cycle are oxidized and released more ATP
- H+
- H+
-
- ATPSYNTHASE
- H+
- H+
- ADEMINE
- 6
- This process made up water and carbon dioxide
- H
-
- 0
-
-
- RIBOSE
- H
- ATP
-
- 0
- P
-
- C
-
-
- P
- 0
-
- P
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
