NEWTON'S LAW OF MOTION
Storyboard Text
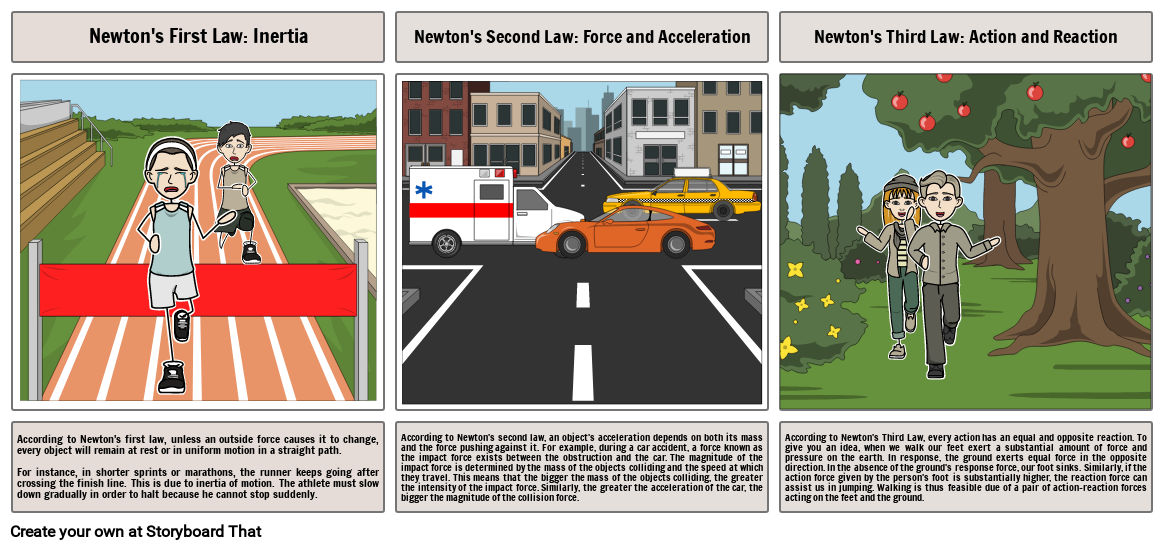
- Newton's First Law: Inertia
- Newton's Second Law: Force and Acceleration
- Newton's Third Law: Action and Reaction
- According to Newton's first law, unless an outside force causes it to change, every object will remain at rest or in uniform motion in a straight path.For instance, in shorter sprints or marathons, the runner keeps going after crossing the finish line. This is due to inertia of motion. The athlete must slow down gradually in order to halt because he cannot stop suddenly.
- According to Newton's second law, an object's acceleration depends on both its mass and the force pushing against it. For example, during a car accident, a force known as the impact force exists between the obstruction and the car. The magnitude of the impact force is determined by the mass of the objects colliding and the speed at which they travel. This means that the bigger the mass of the objects colliding, the greater the intensity of the impact force. Similarly, the greater the acceleration of the car, the bigger the magnitude of the collision force.
- According to Newton's Third Law, every action has an equal and opposite reaction. To give you an idea, when we walk our feet exert a substantial amount of force and pressure on the earth. In response, the ground exerts equal force in the opposite direction. In the absence of the ground's response force, our foot sinks. Similarly, if the action force given by the person's foot is substantially higher, the reaction force can assist us in jumping. Walking is thus feasible due of a pair of action-reaction forces acting on the feet and the ground.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
