Subatomic Particles
Storyboard Text
- Slide: 1
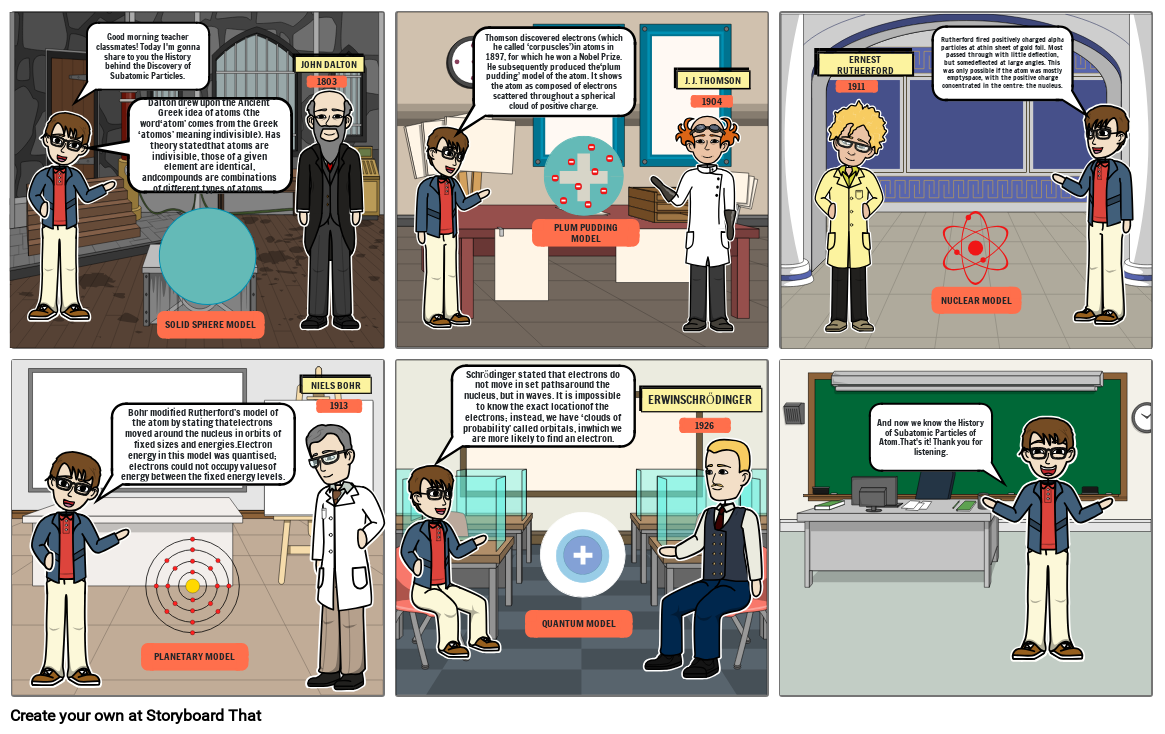
- Good morning teacher classmates! Today I'm gonna share to you the History behind the Discovery of Subatomic Particles.
- JOHN DALTON
- 1803
- Dalton drew upon the Ancient Greek idea of atoms (the word‘atom’ comes from the Greek ‘atomos’ meaning indivisible). Has theory statedthat atoms are indivisible, those of a given element are identical, andcompounds are combinations of different types of atoms.
- Slide: 2
- Thomson discovered electrons (which he called ‘corpuscles’)in atoms in 1897, for which he won a Nobel Prize. He subsequently produced the‘plum pudding’ model of the atom. It shows the atom as composed of electrons scattered throughout a spherical cloud of positive charge.
- J. J. THOMSON
- 1904
- PLUM PUDDING MODEL
- Slide: 3
- Rutherford fired positively charged alpha particles at athin sheet of gold foil. Most passed through with little deflection, but somedeflected at large angles. This was only possible if the atom was mostly emptyspace, with the positive charge concentrated in the centre: the nucleus.
- ERNEST RUTHERFORD
- 1911
- Slide: 4
- SOLID SPHERE MODEL
- NIELS BOHR
- 1913
- Bohr modified Rutherford’s model of the atom by stating thatelectrons moved around the nucleus in orbits of fixed sizes and energies.Electron energy in this model was quantised; electrons could not occupy valuesof energy between the fixed energy levels.
- PLANETARY MODEL
- Slide: 5
- Schrődinger stated that electrons do not move in set pathsaround the nucleus, but in waves. It is impossible to know the exact locationof the electrons; instead, we have ‘clouds of probability’ called orbitals, inwhich we are more likely to find an electron.
- ERWINSCHRŐDINGER
- 1926
- QUANTUM MODEL
- Slide: 6
- NUCLEAR MODEL
- And now we know the History of Subatomic Particles of Atom.That's it! Thank you for listening.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
