Unknown Story
Storyboard Text
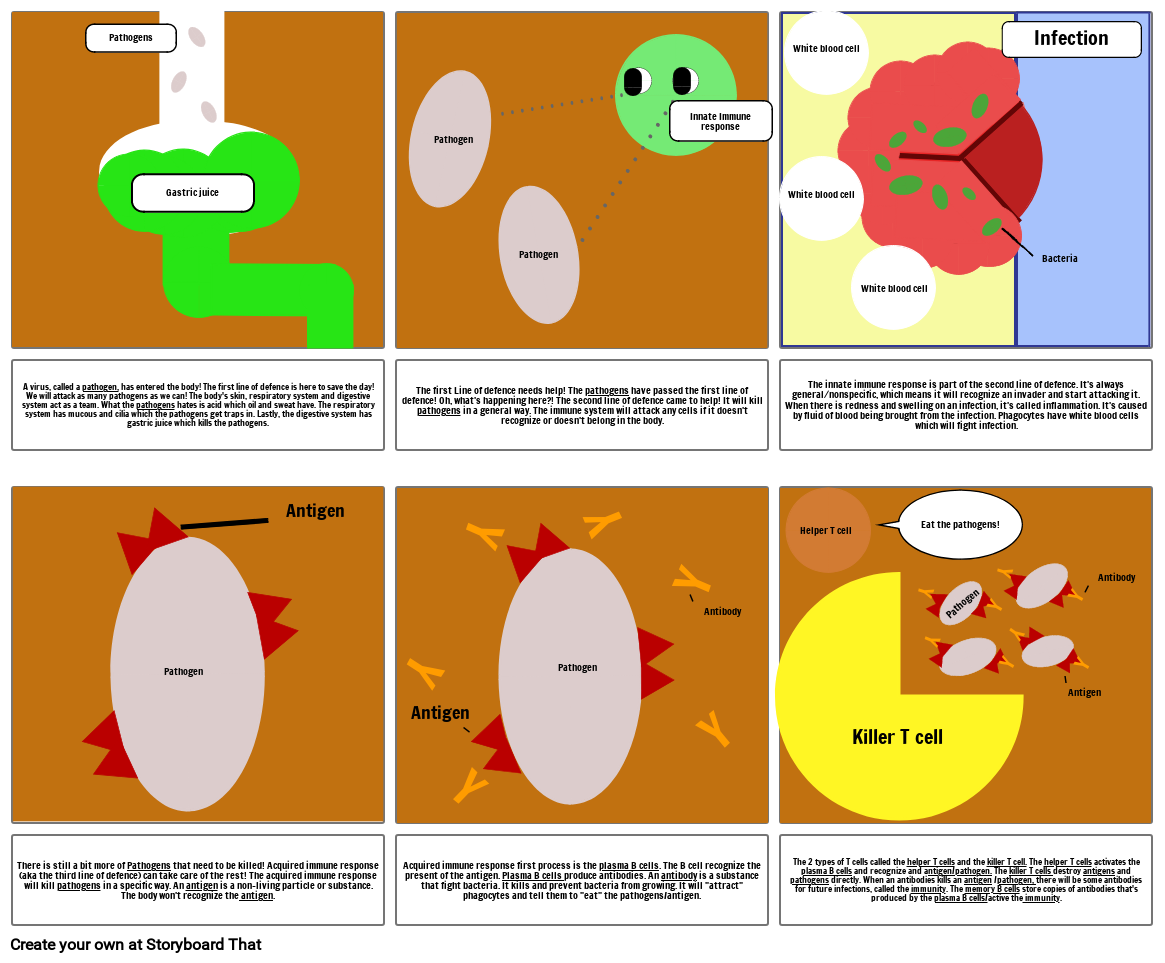
- Pathogens
- Gastric juice
- Pathogen
- Pathogen
- Innate Immune response
- White blood cell
- White blood cell
- White blood cell
- Infection
- Bacteria
- A virus, called a pathogen, has entered the body! The first line of defence is here to save the day! We will attack as many pathogens as we can! The body's skin, respiratory system and digestive system act as a team. What the pathogens hates is acid which oil and sweat have. The respiratory system has mucous and cilia which the pathogens get traps in. Lastly, the digestive system has gastric juice which kills the pathogens.
- Pathogen
- Antigen
- Y
- Antigen
- The first Line of defence needs help! The pathogens have passed the first line of defence! Oh, what's happening here?! The second line of defence came to help! It will kill pathogens in a general way. The immune system will attack any cells if it doesn't recognize or doesn't belong in the body.
- /
- Y
- Pathogen
- Y
- /
- Y
- Y
- Antibody
- The innate immune response is part of the second line of defence. It's always general/nonspecific, which means it will recognize an invader and start attacking it. When there is redness and swelling on an infection, it's called inflammation. It's caused by fluid of blood being brought from the infection. Phagocytes have white blood cells which will fight infection.
- Helper T cell
- Killer T cell
- Eat the pathogens!
- Y
- Y
- Pathogen
- Y
- Y
- Y
- Y
- \
- Antigen
- /
- Y
- Y
- Antibody
- There is still a bit more of Pathogens that need to be killed! Acquired immune response (aka the third line of defence) can take care of the rest! The acquired immune response will kill pathogens in a specific way. An antigen is a non-living particle or substance. The body won't recognize the antigen.
- Acquired immune response first process is the plasma B cells. The B cell recognize the present of the antigen. Plasma B cells produce antibodies. An antibody is a substance that fight bacteria. It kills and prevent bacteria from growing. It will "attract" phagocytes and tell them to "eat" the pathogens/antigen.
- Y
- The 2 types of T cells called the helper T cells and the killer T cell. The helper T cells activates the plasma B cells and recognize and antigen/pathogen. The killer T cells destroy antigens and pathogens directly. When an antibodies kills an antigen /pathogen, there will be some antibodies for future infections, called the immunity. The memory B cells store copies of antibodies that's produced by the plasma B cells/active the immunity.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created

