johnlie1
Storyboard Text
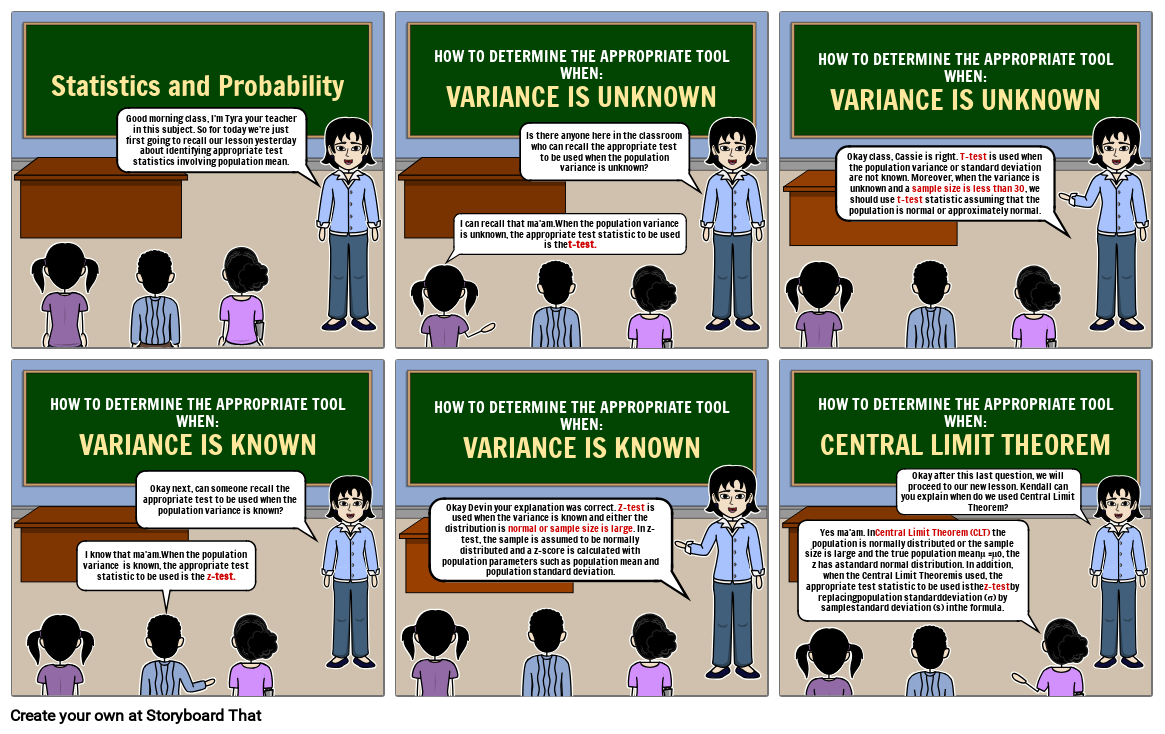
- Slide: 1
- Statistics and Probability
- Good morning class, I'm Tyra your teacher in this subject. So for today we're just first going to recall our lesson yesterday about identifying appropriate test statistics involving population mean.
- Slide: 2
- HOW TO DETERMINE THE APPROPRIATE TOOL WHEN:VARIANCE IS UNKNOWN
- Is there anyone here in the classroom who can recall the appropriate test to be used when the population variance is unknown?
- I can recall that ma'am.When the population variance is unknown, the appropriate test statistic to be used is thet-test.
- Slide: 3
- HOW TO DETERMINE THE APPROPRIATE TOOL WHEN:VARIANCE IS UNKNOWN
- Okay class, Cassie is right. T-test is used when the population variance or standard deviation are not known. Moreover, when the variance is unknown and a sample size is less than 30, we should use t-test statistic assuming that the population is normal or approximately normal.
- Slide: 4
- HOW TO DETERMINE THE APPROPRIATE TOOL WHEN:VARIANCE IS KNOWN
- Okay next, can someone recall the appropriate test to be used when the population variance is known?
- I know that ma'am.When the population variance is known, the appropriate test statistic to be used is the z-test.
- Slide: 5
- HOW TO DETERMINE THE APPROPRIATE TOOL WHEN:VARIANCE IS KNOWN
- Okay Devin your explanation was correct. Z-test is used when the variance is known and either the distribution is normal or sample size is large. In z-test, the sample is assumed to be normally distributed and a z-score is calculated with population parameters such as population mean and population standard deviation.
- Slide: 6
- HOW TO DETERMINE THE APPROPRIATE TOOL WHEN:CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM
- Okay after this last question, we will proceed to our new lesson. Kendall can you explain when do we used Central Limit Theorem?
- Yes ma'am. InCentral Limit Theorem (CLT) the population is normally distributed or the sample size is large and the true population meanμ =μo, the z has astandard normal distribution. In addition, when the Central Limit Theoremis used, the appropriate test statistic to be used isthez-testby replacingpopulation standarddeviation (σ) by samplestandard deviation (s) inthe formula.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
