Modeling Stellar Evolution of a Medium Mass (Sun-Like Star) Amelia Oatman
Storyboard Text
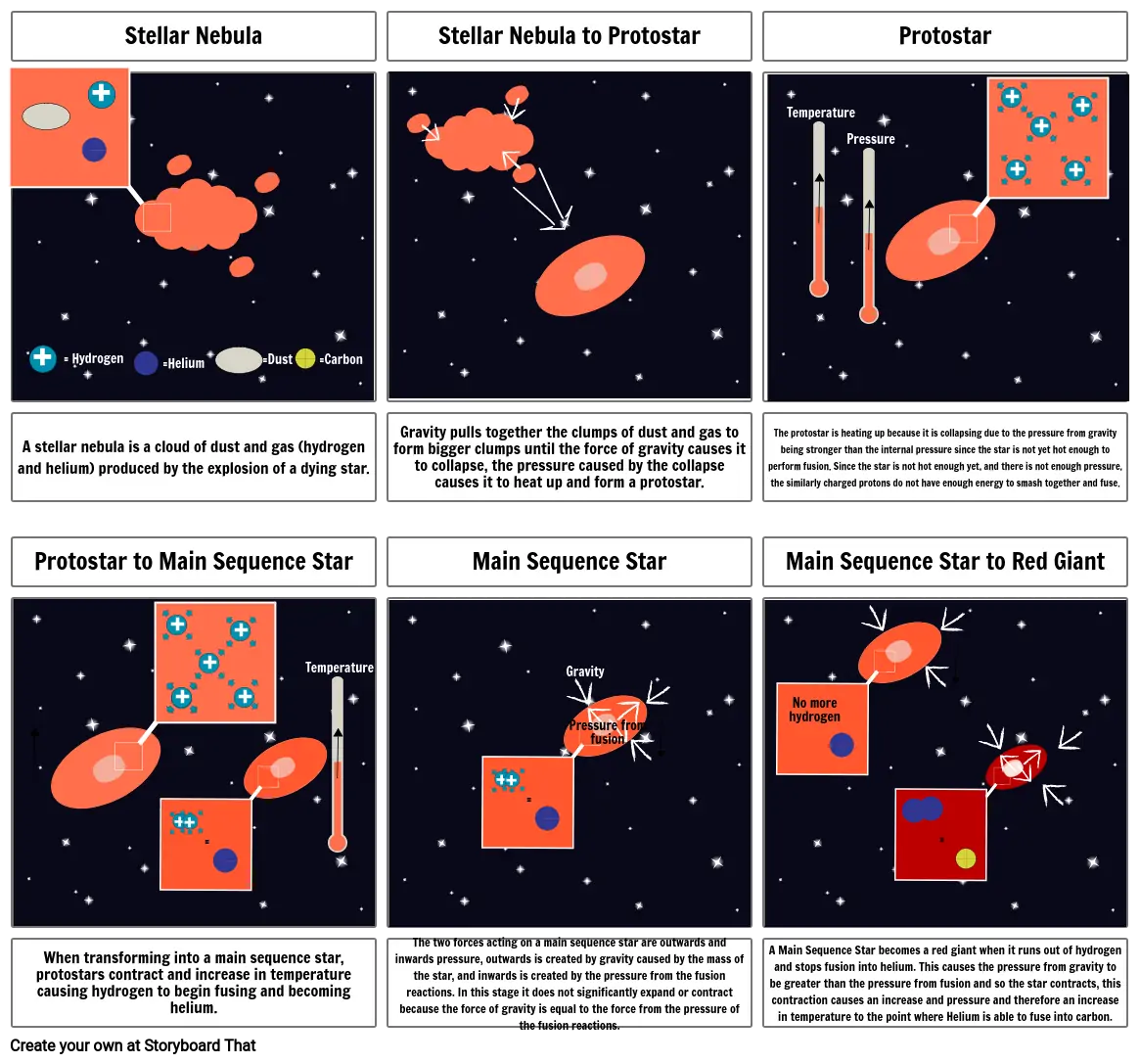
- Stellar Nebula
- = Hydrogen
- =Helium
- =Dust
- =Carbon
- Stellar Nebula to Protostar
- Protostar
- Temperature
- Pressure
- A stellar nebula is a cloud of dust and gas (hydrogen and helium) produced by the explosion of a dying star.
- Protostar to Main Sequence Star
- Temperature
- Gravity pulls together the clumps of dust and gas to form bigger clumps until the force of gravity causes it to collapse, the pressure caused by the collapse causes it to heat up and form a protostar.
- Main Sequence Star
- Gravity
- The protostar is heating up because it is collapsing due to the pressure from gravity being stronger than the internal pressure since the star is not yet hot enough to perform fusion. Since the star is not hot enough yet, and there is not enough pressure, the similarly charged protons do not have enough energy to smash together and fuse.
- Main Sequence Star to Red Giant
- No more hydrogen
- When transforming into a main sequence star, protostars contract and increase in temperature causing hydrogen to begin fusing and becoming helium.
- =
- The two forces acting on a main sequence star are outwards and inwards pressure, outwards is created by gravity caused by the mass of the star, and inwards is created by the pressure from the fusion reactions. In this stage it does not significantly expand or contract because the force of gravity is equal to the force from the pressure of the fusion reactions.
- =
- Pressure from fusion
- A Main Sequence Star becomes a red giant when it runs out of hydrogen and stops fusion into helium. This causes the pressure from gravity to be greater than the pressure from fusion and so the star contracts, this contraction causes an increase and pressure and therefore an increase in temperature to the point where Helium is able to fuse into carbon.
- =
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
