Unknown Story
Storyboard Text
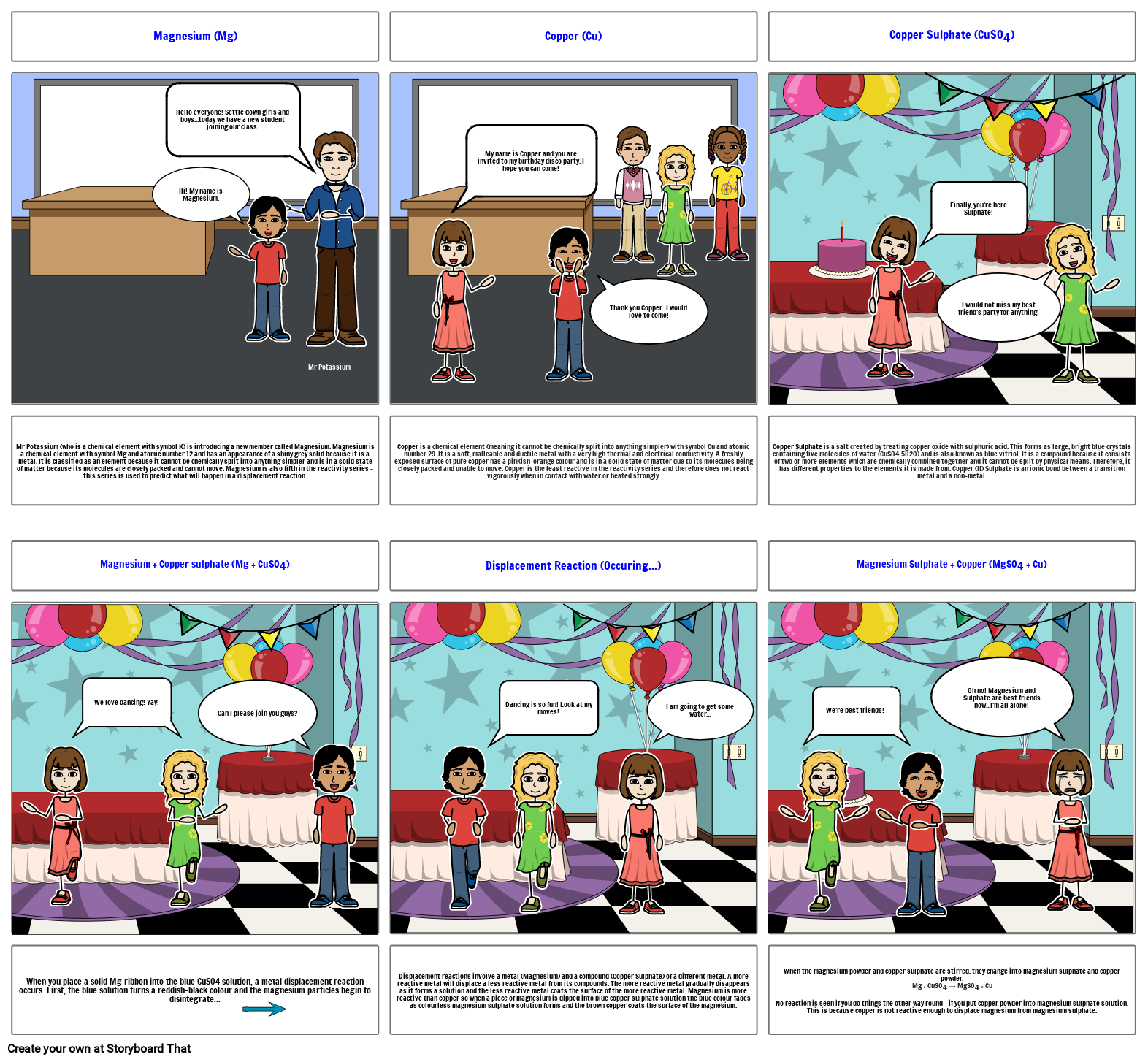
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Hi! My name is Magnesium.
- Hello everyone! Settle down girls and boys...today we have a new student joining our class.
- Mr Potassium
- Copper (Cu)
- My name is Copper and you are invited to my birthday disco party. I hope you can come!
- Thank you Copper...I would love to come!
- Copper Sulphate (CuSO4)
- Finally, you're here Sulphate!
- I would not miss my best friend's party for anything!
- Mr Potassium (who is a chemical element with symbol K) is introducing a new member called Magnesium. Magnesium is a chemical element with symbol Mg and atomic number 12 and has an appearance of a shiny grey solid because it is a metal. It is classified as an element because it cannot be chemically split into anything simpler and is in a solid state of matter because its molecules are closely packed and cannot move. Magnesium is also fifth in the reactivity series - this series is used to predict what will happen in a displacement reaction.
- Magnesium + Copper sulphate (Mg + CuSO4)
- We love dancing! Yay!
- Can I please join you guys?
- Copper is a chemical element (meaning it cannot be chemically split into anything simpler) with symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable and ductile metal with a very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange colour and is in a solid state of matter due to its molecules being closely packed and unable to move. Copper is the least reactive in the reactivity series and therefore does not react vigorously when in contact with water or heated strongly.
- Displacement Reaction (Occuring...)
- Dancing is so fun! Look at my moves!
- I am going to get some water...
- Copper Sulphate is a salt created by treating copper oxide with sulphuric acid. This forms as large, bright blue crystals containing five molecules of water (CuSO4∙5H2O) and is also known as blue vitriol. It is a compound because it consists of two or more elements which are chemically combined together and it cannot be split by physical means. Therefore, it has different properties to the elements it is made from. Copper (II) Sulphate is an ionic bond between a transition metal and a non-metal.
- Magnesium Sulphate + Copper (MgSO4 + Cu)
- We're best friends!
- Oh no! Magnesium and Sulphate are best friends now...I'm all alone!
- When you place a solid Mg ribbon into the blue CuSO4 solution, a metal displacement reaction occurs. First, the blue solution turns a reddish-black colour and the magnesium particles begin to disintegrate...
- Displacement reactions involve a metal (Magnesium) and a compound (Copper Sulphate) of a different metal. A more reactive metal will displace a less reactive metal from its compounds. The more reactive metal gradually disappears as it forms a solution and the less reactive metal coats the surface of the more reactive metal. Magnesium is more reactive than copper so when a piece of magnesium is dipped into blue copper sulphate solution the blue colour fades as colourless magnesium sulphate solution forms and the brown copper coats the surface of the magnesium.
- When the magnesium powder and copper sulphate are stirred, they change into magnesium sulphate and copper powder.Mg + CuSO4 → MgSO4 + Cu No reaction is seen if you do things the other way round – if you put copper powder into magnesium sulphate solution. This is because copper is not reactive enough to displace magnesium from magnesium sulphate.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
