Periodic Trends Cartoon Part 2
Storyboard Text
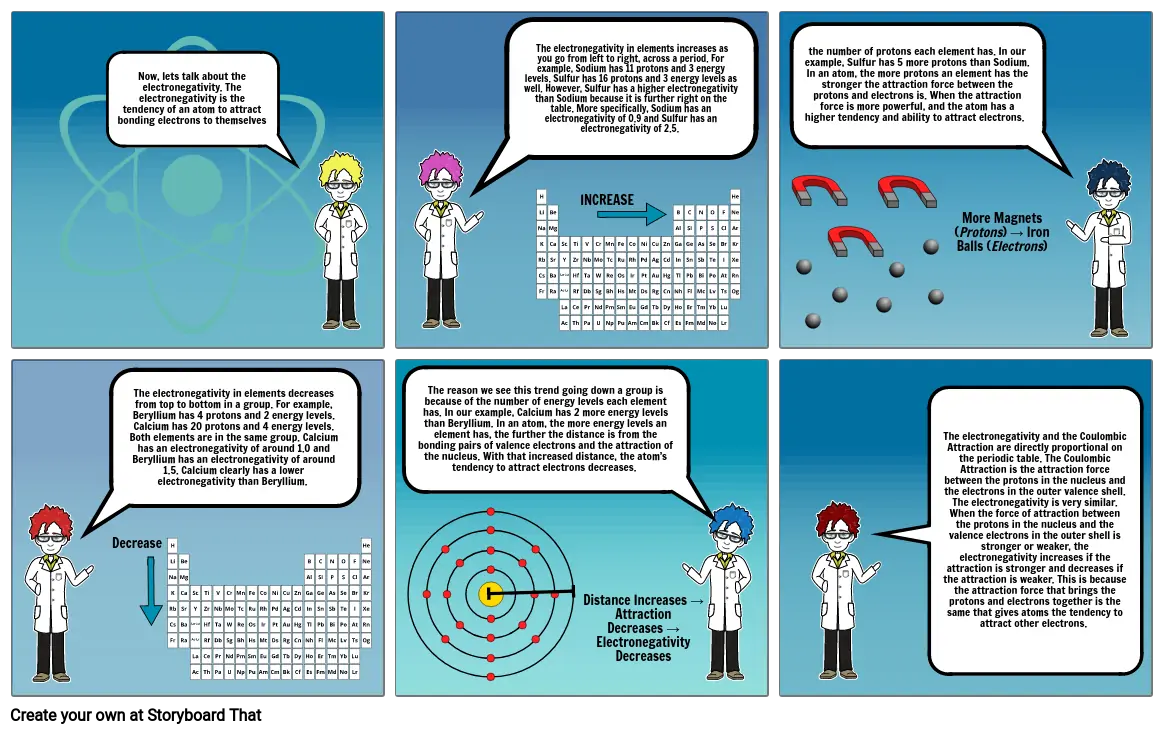
- Now, lets talk about the electronegativity. The electronegativity is the tendency of an atom to attract bonding electrons to themselves
- The electronegativity in elements increases as you go from left to right, across a period. For example, Sodium has 11 protons and 3 energy levels. Sulfur has 16 protons and 3 energy levels as well. However, Sulfur has a higher electronegativity than Sodium because it is further right on the table. More specifically, Sodium has an electronegativity of 0.9 and Sulfur has an electronegativity of 2.5.
- INCREASE
- the number of protons each element has. In our example, Sulfur has 5 more protons than Sodium. In an atom, the more protons an element has the stronger the attraction force between the protons and electrons is. When the attraction force is more powerful, and the atom has a higher tendency and ability to attract electrons.
- More Magnets (Protons) → Iron Balls (Electrons)
- The electronegativity in elements decreases from top to bottom in a group. For example, Beryllium has 4 protons and 2 energy levels. Calcium has 20 protons and 4 energy levels. Both elements are in the same group. Calcium has an electronegativity of around 1.0 and Beryllium has an electronegativity of around 1.5. Calcium clearly has a lower electronegativity than Beryllium.
- Decrease
- The reason we see this trend going down a group is because of the number of energy levels each element has. In our example, Calcium has 2 more energy levels than Beryllium. In an atom, the more energy levels an element has, the further the distance is from the bonding pairs of valence electrons and the attraction of the nucleus. With that increased distance, the atom’s tendency to attract electrons decreases.
- Distance Increases → Attraction Decreases → Electronegativity Decreases
- The electronegativity and the Coulombic Attraction are directly proportional on the periodic table. The Coulombic Attraction is the attraction force between the protons in the nucleus and the electrons in the outer valence shell. The electronegativity is very similar. When the force of attraction between the protons in the nucleus and the valence electrons in the outer shell is stronger or weaker, the electronegativity increases if the attraction is stronger and decreases if the attraction is weaker. This is because the attraction force that brings the protons and electrons together is the same that gives atoms the tendency to attract other electrons.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
