Unknown Story
Storyboard Text
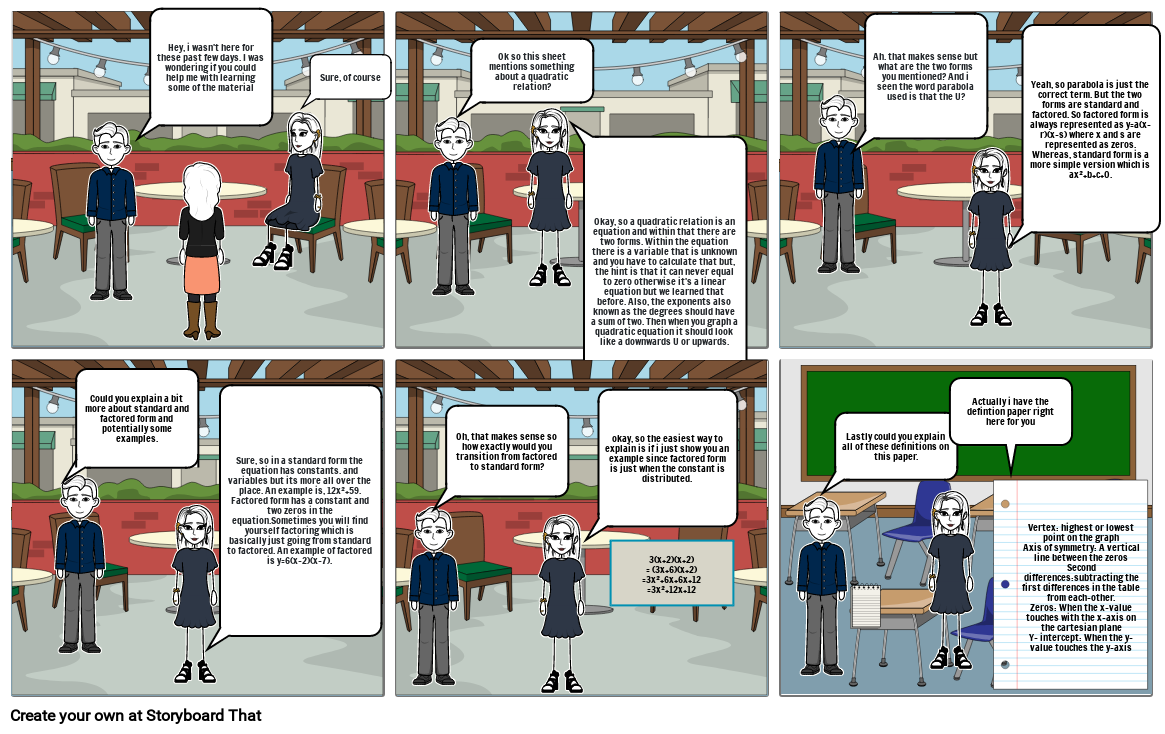
- Hi, Anna i was absent yesterday because i was sick, can you help me about the lessons yesterday?
- Sure, of course
- Ok so this sheet mentions something about a parabola?
- Okay, so a parabola a plane curve generated by a point moving so that its distance from a fixed point is equal to its distance from a fixed line : the intersection of a right circular cone with a plane parallel to an element of the cone.
- Ah. that makes sense but what are the two forms you mentioned? And i seen the word parabola used is that the U?
- Yeah, so parabola is just the correct term. But the two forms are standard and factored. So factored form is always represented as y=a(x-r)(x-s) where x and s are represented as zeros. Whereas, standard form is a more simple version which is ax²+b+c+0.
- Could you explain a bit more about standard and factored form and potentially some examples.
- Sure, so in a standard form the equation has constants. and variables but its more all over the place. An example is, 12x²+59. Factored form has a constant and two zeros in the equation.Sometimes you will find yourself factoring which is basically just going from standard to factored. An example of factored is y=6(x-2)(x-7).
- Oh, that makes sense so how exactly would you transition from factored to standard form?
- okay, so the easiest way to explain is if i just show you an example since factored form is just when the constant is distributed.
- 3(x+2)(x+2)= (3x+6)(x+2)=3x²+6x+6x+12=3x²+12x+12
- Lastly could you explain all of these definitions on this paper.
- Actually i have the defintion paper right here for you
- Vertex: highest or lowest point on the graphAxis of symmetry: A vertical line between the zerosSecond differences:subtracting the first differences in the table from each-other.Zeros: When the x-value touches with the x-axis on the cartesian planeY- intercept: When the y-value touches the y-axis
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created

