The Segregated South
Storyboard Text
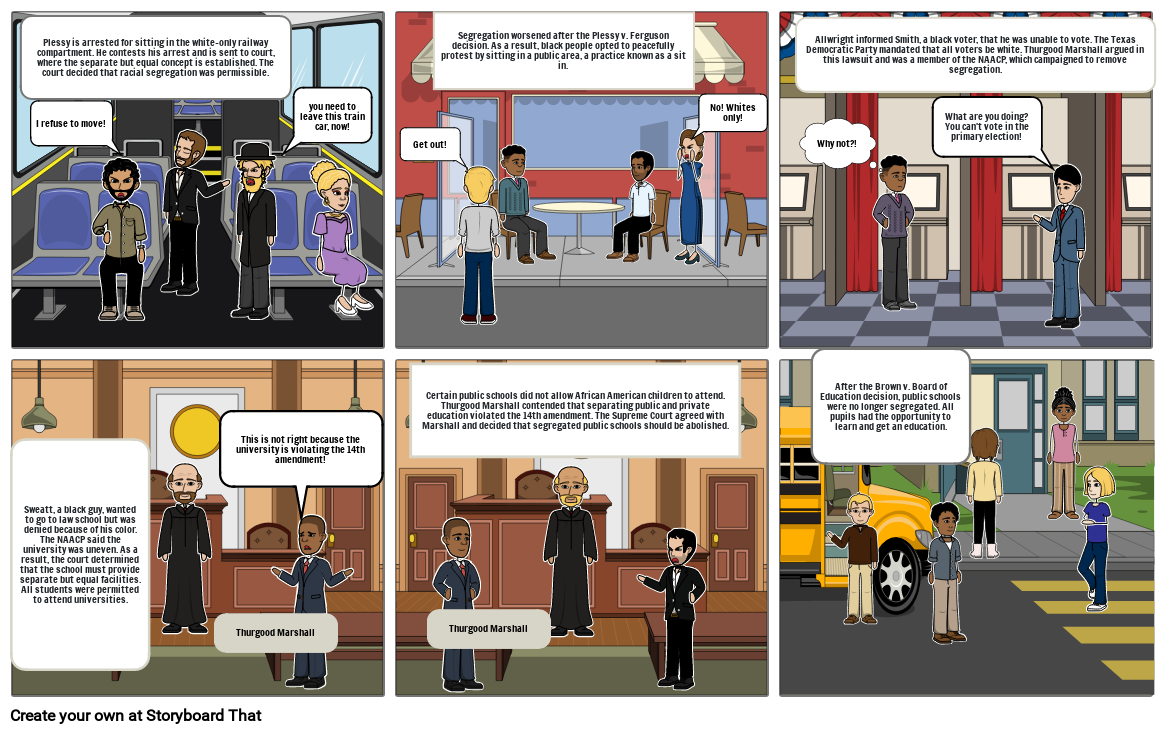
- Plessy is arrested for sitting in the white-only railway compartment. He contests his arrest and is sent to court, where the separate but equal concept is established. The court decided that racial segregation was permissible.
- I refuse to move!
- you need to leave this train car, now!
- Get out!
- Segregation worsened after the Plessy v. Ferguson decision. As a result, black people opted to peacefully protest by sitting in a public area, a practice known as a sit in.
- No! Whites only!
- Allwright informed Smith, a black voter, that he was unable to vote. The Texas Democratic Party mandated that all voters be white. Thurgood Marshall argued in this lawsuit and was a member of the NAACP, which campaigned to remove segregation.
- Why not?!
- After the Brown v. Board of Education decision, public schools were no longer segregated. All pupils had the opportunity to learn and get an education.
- What are you doing? You can't vote in the primary election!
- Sweatt, a black guy, wanted to go to law school but was denied because of his color. The NAACP said the university was uneven. As a result, the court determined that the school must provide separate but equal facilities. All students were permitted to attend universities.
- Thurgood Marshall
- This is not right because the university is violating the 14th amendment!
- Certain public schools did not allow African American children to attend. Thurgood Marshall contended that separating public and private education violated the 14th amendment. The Supreme Court agreed with Marshall and decided that segregated public schools should be abolished.
- Thurgood Marshall
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
