GEN BIO
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus Basics
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Nucleus can be describes as the process and administrative control center for the cell.
- A Nucleus is only found in Eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus
The first organelle we will cover is the nucleus.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- Four Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
ORGANELLES: The NucleusFunction
- The Nucleus has two functions:
1) The Nucleus stores heredity material, DNA, as Chromatin.
2) The Nucleus coordinates cell activities, suchas growth and reproduction of the cell, intermediate metabolism, and protein synthesis.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Function of this organelle was determined by Rudolph Virchow.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- For Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
So, What is the Nucleus? In 1833, Robert Brown discovered and named the nucleus while observing plant cells. A nucleus is an organelle that controls almost the whole cell.
These are the four major things that make up the nucleus. But what are they and what do they do?
The Nucleolus is found floating inside of the nucleoplasm, where it spends it time making ribosomes.
Next, Nucleoplasm is like the cytoplasm for the nucleus. It fills the nucleus and gives it from.
The nuclear envelope is the membrane that surrounds all of the contents of the nucleus. It has pores allowing molecules to exit and enter as they please. It also is made up of two layers of membrane with an "airy" space in between.
Finally, Chromatin is the last major thing contained inside of the nucleus. Chromatin is simply a protein called DNA.
The Nucleus only has two functions. These are to store DNA as Chromatin + coordinate cellular activity.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus Basics
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Nucleus can be describes as the process and administrative control center for the cell.
- A Nucleus is only found in Eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus
The first organelle we will cover is the nucleus.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- Four Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
ORGANELLES: The NucleusFunction
- The Nucleus has two functions:
1) The Nucleus stores heredity material, DNA, as Chromatin.
2) The Nucleus coordinates cell activities, suchas growth and reproduction of the cell, intermediate metabolism, and protein synthesis.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Function of this organelle was determined by Rudolph Virchow.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- For Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
So, What is the Nucleus? In 1833, Robert Brown discovered and named the nucleus while observing plant cells. A nucleus is an organelle that controls almost the whole cell.
These are the four major things that make up the nucleus. But what are they and what do they do?
The Nucleolus is found floating inside of the nucleoplasm, where it spends it time making ribosomes.
Next, Nucleoplasm is like the cytoplasm for the nucleus. It fills the nucleus and gives it from.
The nuclear envelope is the membrane that surrounds all of the contents of the nucleus. It has pores allowing molecules to exit and enter as they please. It also is made up of two layers of membrane with an "airy" space in between.
Finally, Chromatin is the last major thing contained inside of the nucleus. Chromatin is simply a protein called DNA.
The Nucleus only has two functions. These are to store DNA as Chromatin + coordinate cellular activity.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus Basics
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Nucleus can be describes as the process and administrative control center for the cell.
- A Nucleus is only found in Eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus
The first organelle we will cover is the nucleus.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- Four Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
ORGANELLES: The NucleusFunction
- The Nucleus has two functions:
1) The Nucleus stores heredity material, DNA, as Chromatin.
2) The Nucleus coordinates cell activities, suchas growth and reproduction of the cell, intermediate metabolism, and protein synthesis.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Function of this organelle was determined by Rudolph Virchow.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- For Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
So, What is the Nucleus? In 1833, Robert Brown discovered and named the nucleus while observing plant cells. A nucleus is an organelle that controls almost the whole cell.
These are the four major things that make up the nucleus. But what are they and what do they do?
The Nucleolus is found floating inside of the nucleoplasm, where it spends it time making ribosomes.
Next, Nucleoplasm is like the cytoplasm for the nucleus. It fills the nucleus and gives it from.
The nuclear envelope is the membrane that surrounds all of the contents of the nucleus. It has pores allowing molecules to exit and enter as they please. It also is made up of two layers of membrane with an "airy" space in between.
Finally, Chromatin is the last major thing contained inside of the nucleus. Chromatin is simply a protein called DNA.
The Nucleus only has two functions. These are to store DNA as Chromatin + coordinate cellular activity.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus Basics
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Nucleus can be describes as the process and administrative control center for the cell.
- A Nucleus is only found in Eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus
The first organelle we will cover is the nucleus.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- Four Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
ORGANELLES: The NucleusFunction
- The Nucleus has two functions:
1) The Nucleus stores heredity material, DNA, as Chromatin.
2) The Nucleus coordinates cell activities, suchas growth and reproduction of the cell, intermediate metabolism, and protein synthesis.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Function of this organelle was determined by Rudolph Virchow.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- For Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
So, What is the Nucleus? In 1833, Robert Brown discovered and named the nucleus while observing plant cells. A nucleus is an organelle that controls almost the whole cell.
These are the four major things that make up the nucleus. But what are they and what do they do?
The Nucleolus is found floating inside of the nucleoplasm, where it spends it time making ribosomes.
Next, Nucleoplasm is like the cytoplasm for the nucleus. It fills the nucleus and gives it from.
The nuclear envelope is the membrane that surrounds all of the contents of the nucleus. It has pores allowing molecules to exit and enter as they please. It also is made up of two layers of membrane with an "airy" space in between.
Finally, Chromatin is the last major thing contained inside of the nucleus. Chromatin is simply a protein called DNA.
The Nucleus only has two functions. These are to store DNA as Chromatin + coordinate cellular activity.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus Basics
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Nucleus can be describes as the process and administrative control center for the cell.
- A Nucleus is only found in Eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus
The first organelle we will cover is the nucleus.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- Four Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
ORGANELLES: The NucleusFunction
- The Nucleus has two functions:
1) The Nucleus stores heredity material, DNA, as Chromatin.
2) The Nucleus coordinates cell activities, suchas growth and reproduction of the cell, intermediate metabolism, and protein synthesis.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Function of this organelle was determined by Rudolph Virchow.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- For Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
So, What is the Nucleus? In 1833, Robert Brown discovered and named the nucleus while observing plant cells. A nucleus is an organelle that controls almost the whole cell.
These are the four major things that make up the nucleus. But what are they and what do they do?
The Nucleolus is found floating inside of the nucleoplasm, where it spends it time making ribosomes.
Next, Nucleoplasm is like the cytoplasm for the nucleus. It fills the nucleus and gives it from.
The nuclear envelope is the membrane that surrounds all of the contents of the nucleus. It has pores allowing molecules to exit and enter as they please. It also is made up of two layers of membrane with an "airy" space in between.
Finally, Chromatin is the last major thing contained inside of the nucleus. Chromatin is simply a protein called DNA.
The Nucleus only has two functions. These are to store DNA as Chromatin + coordinate cellular activity.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus Basics
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Nucleus can be describes as the process and administrative control center for the cell.
- A Nucleus is only found in Eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus
The first organelle we will cover is the nucleus.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- Four Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
ORGANELLES: The NucleusFunction
- The Nucleus has two functions:
1) The Nucleus stores heredity material, DNA, as Chromatin.
2) The Nucleus coordinates cell activities, suchas growth and reproduction of the cell, intermediate metabolism, and protein synthesis.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Function of this organelle was determined by Rudolph Virchow.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- For Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
So, What is the Nucleus? In 1833, Robert Brown discovered and named the nucleus while observing plant cells. A nucleus is an organelle that controls almost the whole cell.
These are the four major things that make up the nucleus. But what are they and what do they do?
The Nucleolus is found floating inside of the nucleoplasm, where it spends it time making ribosomes.
Next, Nucleoplasm is like the cytoplasm for the nucleus. It fills the nucleus and gives it from.
The nuclear envelope is the membrane that surrounds all of the contents of the nucleus. It has pores allowing molecules to exit and enter as they please. It also is made up of two layers of membrane with an "airy" space in between.
Finally, Chromatin is the last major thing contained inside of the nucleus. Chromatin is simply a protein called DNA.
The Nucleus only has two functions. These are to store DNA as Chromatin + coordinate cellular activity.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus Basics
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Nucleus can be describes as the process and administrative control center for the cell.
- A Nucleus is only found in Eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus
The first organelle we will cover is the nucleus.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- Four Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
ORGANELLES: The NucleusFunction
- The Nucleus has two functions:
1) The Nucleus stores heredity material, DNA, as Chromatin.
2) The Nucleus coordinates cell activities, suchas growth and reproduction of the cell, intermediate metabolism, and protein synthesis.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
-Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cellsin 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.
- The Function of this organelle was determined by Rudolph Virchow.
ORGANELLES: The Nucleus
- For Major Components:
1) Nucleolus
2) Nucleoplasm
3) Nuclear Envelope
4) Chromatin
So, What is the Nucleus? In 1833, Robert Brown discovered and named the nucleus while observing plant cells. A nucleus is an organelle that controls almost the whole cell.
These are the four major things that make up the nucleus. But what are they and what do they do?
The Nucleolus is found floating inside of the nucleoplasm, where it spends it time making ribosomes.
Next, Nucleoplasm is like the cytoplasm for the nucleus. It fills the nucleus and gives it from.
The nuclear envelope is the membrane that surrounds all of the contents of the nucleus. It has pores allowing molecules to exit and enter as they please. It also is made up of two layers of membrane with an "airy" space in between.
Finally, Chromatin is the last major thing contained inside of the nucleus. Chromatin is simply a protein called DNA.
The Nucleus only has two functions. These are to store DNA as Chromatin + coordinate cellular activity.
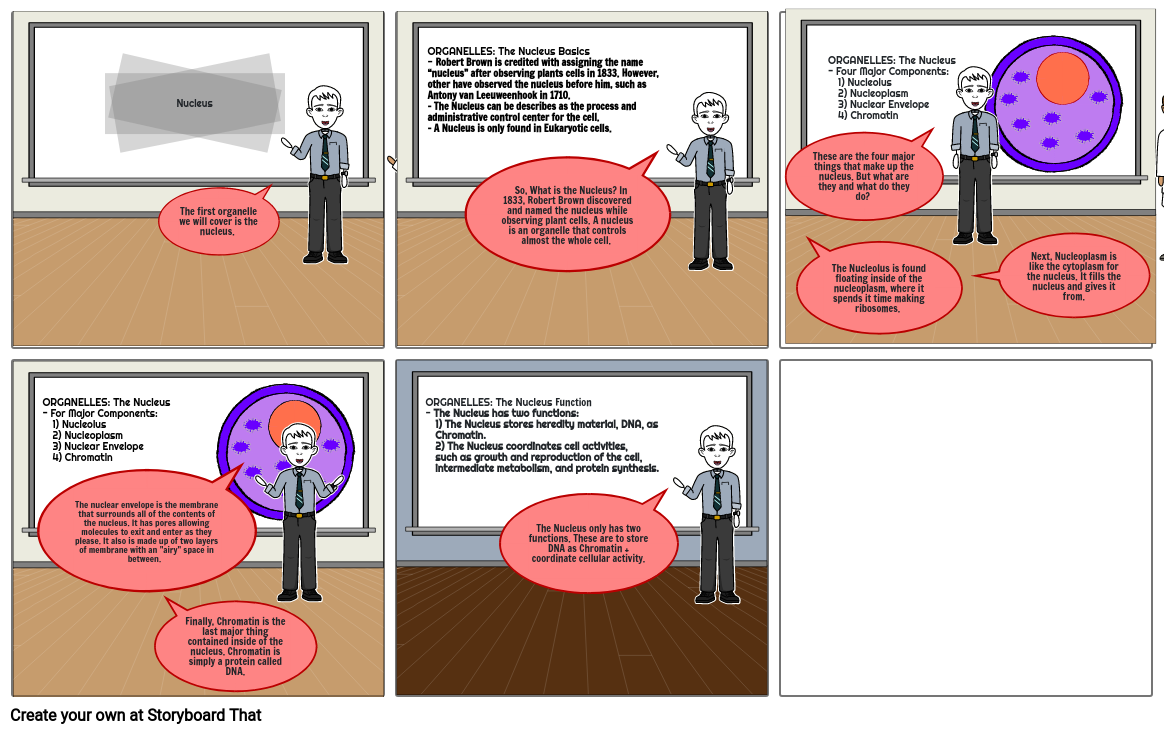
Storyboard Text
-
- Nucleus
- The first organelle we will cover is the nucleus.
- ORGANELLES: The Nucleus Basics - Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cells in 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710.- The Nucleus can be describes as the process and administrative control center for the cell. - A Nucleus is only found in Eukaryotic cells.
- So, What is the Nucleus? In 1833, Robert Brown discovered and named the nucleus while observing plant cells. A nucleus is an organelle that controls almost the whole cell.
- These are the four major things that make up the nucleus. But what are they and what do they do?
- The Nucleolus is found floating inside of the nucleoplasm, where it spends it time making ribosomes.
- ORGANELLES: The Nucleus- Four Major Components: 1) Nucleolus 2) Nucleoplasm 3) Nuclear Envelope 4) Chromatin
- Next, Nucleoplasm is like the cytoplasm for the nucleus. It fills the nucleus and gives it from.
-
- ORGANELLES: The Nucleus- For Major Components: 1) Nucleolus 2) Nucleoplasm 3) Nuclear Envelope 4) Chromatin
- ORGANELLES: The Nucleus - Robert Brown is credited with assigning the name “nucleus” after observing plants cells in 1833. However, other have observed the nucleus before him, such as Antony van Leeuweenhook in 1710. - The Function of this organelle was determined by Rudolph Virchow.
- The nuclear envelope is the membrane that surrounds all of the contents of the nucleus. It has pores allowing molecules to exit and enter as they please. It also is made up of two layers of membrane with an "airy" space in between.
- Finally, Chromatin is the last major thing contained inside of the nucleus. Chromatin is simply a protein called DNA.
- ORGANELLES: The Nucleus Function- The Nucleus has two functions: 1) The Nucleus stores heredity material, DNA, as Chromatin. 2) The Nucleus coordinates cell activities, such as growth and reproduction of the cell, intermediate metabolism, and protein synthesis.
- The Nucleus only has two functions. These are to store DNA as Chromatin + coordinate cellular activity.


