Final Culminating Project!
Storyboard Text
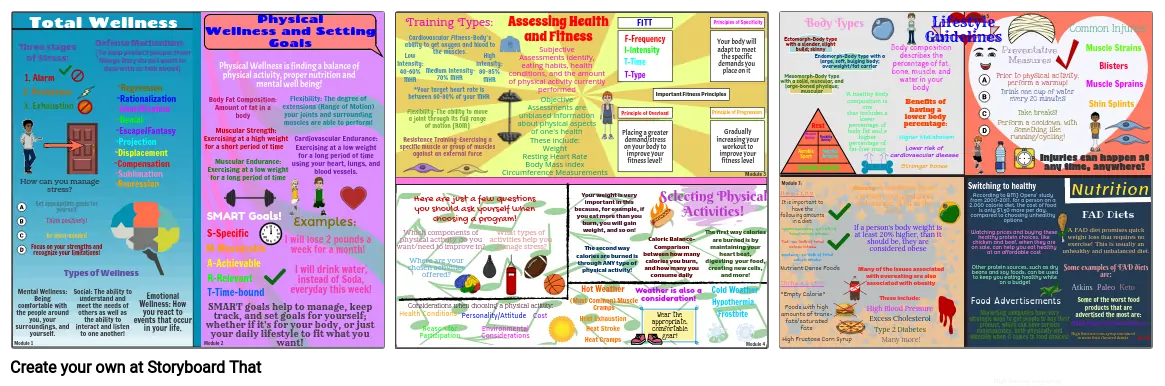
- Total Wellness
- Module 1
- 1. Alarm
- Three stages of Stress:
- 2. Resistance
- 3. Exhaustion
- Types of Wellness
- Defense Mechanisms (To help protect people from things they do not want to deal with or talk about)
- Mental Wellness: Being comfortable with the people around you, your surroundings, and yourself. Social: The ability to understand and meet the needs of others as well as the ability to interact and listen to one another! Emotional Wellness: How you react to events that occur in your life.
- How can you manage stress? Set appropriate goals for yourself Think positively! Be open-minded Focus on your strengths and recognize your limitations!
- Physical Wellness and Setting Goals
- ~Rationalization
- ~Escape/Fantasy
- ~Identification
- ~Denial
- ~Compensation
- ~Projection
- ~Repression
- ~Sublimation
- ~Displacement
- ~Regression
- Module 2
- S-Specific
- R-Relevant
- A-Achievable
- M-Measurable
- T-Time-bound
- SMART Goals!
- Muscular Strength: Exercising at a high weight for a short period of time
- Muscular Endurance: Exercising at a low weight for a long period of time
-
- SMART goals help to manage, keep track, and set goals for yourself; whether if it's for your body, or just your daily lifestyle to fit what you want!
- Body Fat Composition: Amount of fat in a body
- Physical Wellness is finding a balance of physical activity, proper nutrition and mental well being!
- These include:WeightResting Heart RateBody Mass IndexCircumference Measurements
- Flexibility: The degree of extensions (Range of Motion) your joints and surrounding muscles are able to perform!
- Examples:
- I will lose 2 pounds a week for a month!
- I will drink water, instead of Soda, everyday this week!
- Here are just a few questions you should ask yourself when choosing a program!
- Cardiovascular Endurance: Exercising at a low weight for a long period of time using your heart, lungs, and blood vessels.
- Resistance Training-Exercising a specific muscle or group of muscles against an external force
- Which components of physical activity do you want/need to improve in?
- Training Types:
- Cardiovascular Fitness-Body's ability to get oxygen and blood to the muscles.
- Flexibility-The ability to move a joint through its full range of motion (ROM)
- Where are your chosen activities offered?
- Low Intensity:40-60% MHR
- Medium Intensity-70% MHR
- Health Conditions
- Considerations when choosing a physical activity:
- Reason for Participation
- *Your target heart rate is between 60-80% of your MHR
- Assessing Health and Fitness
- Subjective Assessments identify, eating habits, health conditions, and the amount of physical activity currently performed
- What types of activities help you manage stress?
- Objective Assessments are unbiased information about physical aspects of one's health
- High Intensity: 80-85% MHR
- Personality/Attitude
- Environmental Considerations
- Cost
- Selecting Physical Activities!
- Hot Weather
- Heat Exhaustion
- Heat Stroke
- Heat Cramps
- (Most Common) Muscle Cramps
- FITT
- Your weight is very important in this because, for example, if you eat more than you burn, you will gain weight, and so on!
- The second way calories are burned is through ANY type of physical activity!
- T-Time
- T-Type
- I-Intensity
- F-Frequency
- Principle of Overload
- Placing a greater demand/stress on your body to improve your fitness level!
- Weather is also a consideration!
-
- Caloric Balance-Comparison between how many calories you burn, and how many you consume daily
-
- Important Fitness Principles
- Wear the appropriate, comfortable gear!
- Principle of Progression
- Module 3
- Module 4
-
- Hypothermia
- Frostbite
- Cold Weather
- Principles of Specificity
- The first way calories are burned is by maintaining your heart beat, digesting your food, creating new cells, and more!
- Module 7:
- Gradually increasing your workout to improve your fitness level
- Your body will adapt to meet the specific demands you place on it
- Mesomorph-Body type with a solid, muscular, and large-boned physique; muscular
- Ectomorph-Body type with a slender, slight build; skinny
- Endomorph-Body type with a large, soft, bulging body; overweight/fat carrier
- Body Types
- Healthy
- Unhealthy
- "Empty Calorie"
- Aerobic Sport
- Muscular Activity
- Nutrient Dense Foods
- Lifestyle Activity
- High Fructose Corn Syrup
- Rest
- Fat: 20-35% of total caloric intake
- Carbohydrates: 45-65% of total caloric intake
- Proteins: 10-35% of total caloric intake
- It is important to have the following amounts in a diet:
- Foods with high amounts of trans-fats/saturated fats
- Flexibility Activity
- Aerobic Activity
-
-
- A healthy body composition is one that includes a lower percentage of body fat and a higher percentage of fat-free mass
- Lower risk of cardiovascular disease
- Stronger bones
- Body composition describes the percentage of fat, bone, muscle, and water in your body
-
- Higher Metabolism
- Lifestyle Guidelines
- Benefits of having a lower body percentage:
- Obesity-A condition by an excessive accumulation and storage of fat in the body
- If a person's body weight is at least 20% higher, than it should be, they are considered obese
- These include:
- High Blood Pressure
- Excess Cholesterol
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Many of the issues associated with overeating are also associated with obesity
- Many more!
- Module 5
- Injuries can happen at any time, anywhere!
-
- Switching to healthy
- According to BMJ Opens' study from 2000-2011, for a person on a 2,000 calorie diet, the cost of food is only $1.50 more per day, compared to choosing unhealthy options
- Watching prices and buying these healthy protein choices, like chicken and beef, when they are on sale, can help you eat healthy at an affordable cost
- Marketing companies have very strategic ways to get people to buy their product, which can have serious consequences, both physically and mentally when it comes to food choices!
- Other protein sources, such as dry beans and soy foods, can be used to keep you eating healthy while on a budget
- Food Advertisements
- Preventative Measures Prior to physical activity, perform a warmup! Drink one cup of water every 20 minutes Take breaks! Perform a cooldown, with something like running/cycling!
- High fructose corn syrup contained in fruit flavored drinks
- Common Injuries:
- Muscle Strains
- Shin Splints
- Blisters
- Muscle Sprains
- Atkins
- A FAD diet promises quick weight loss that requires no exercise! This is usually an unhealthy and unbalanced diet.
- Some examples of FAD diets are:
- Paleo
- FAD Diets
- High Sugar Cereal Products
- Nutrition
- Some of the worst food products that are advertised the most are:
- High fructose corn syrup contained in most fruit flavored drinks
- Keto
- Soda
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
