Unknown Story
Storyboard Text
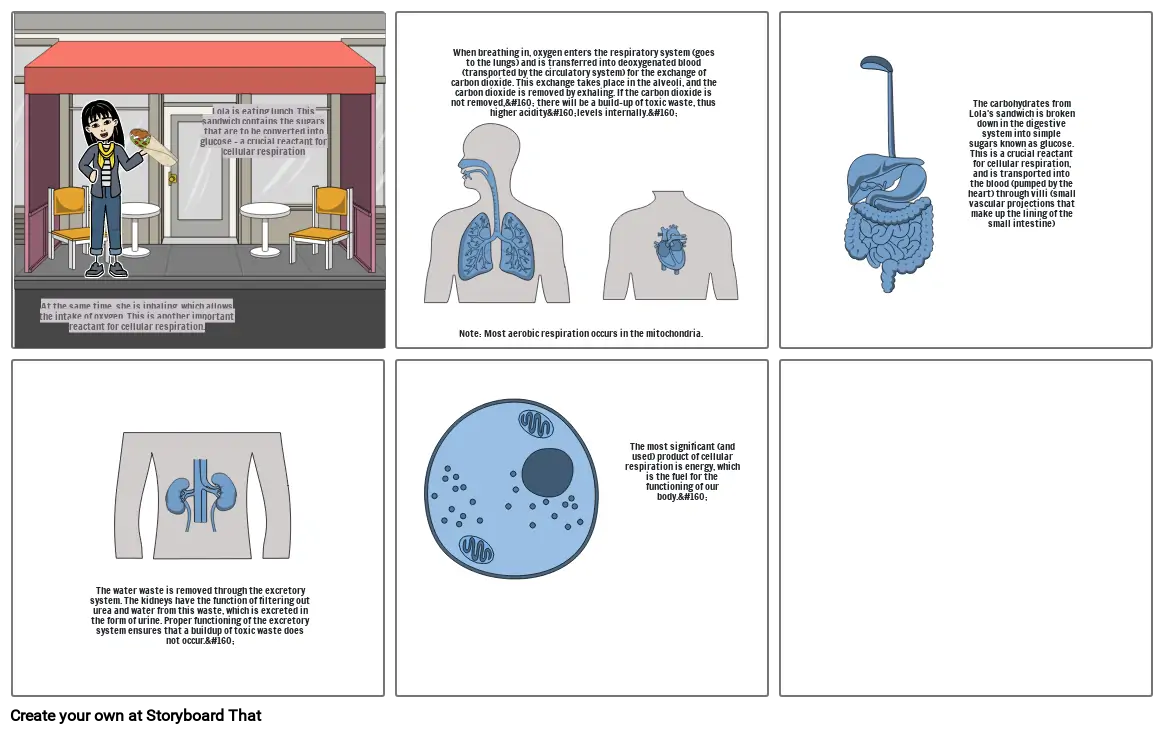
- At the same time, she is inhaling, which allows the intake of oxygen. This is another important reactant for cellular respiration.
- Lola is eating lunch. This sandwich contains the sugars that are to be converted into glucose - a crucial reactant for cellular respiration
- Note: Most aerobic respiration occurs in the mitochondria.
- When breathing in, oxygen enters the respiratory system (goes to the lungs) and is transferred into deoxygenated blood (transported by the circulatory system) for the exchange of carbon dioxide. This exchange takes place in the alveoli, and the carbon dioxide is removed by exhaling. If the carbon dioxide is not removed, there will be a build-up of toxic waste, thus higher aciditylevels internally.
- The carbohydrates from Lola's sandwich is broken down in the digestive system into simple sugars known as glucose. This is a crucial reactant for cellular respiration, and is transported into the blood (pumped by the heart) through villi (small vascular projections that make up the lining of the small intestine)
- The water waste is removed through the excretory system. The kidneys have the function of filtering out urea and water from this waste, which is excreted in the form of urine. Proper functioning of the excretory system ensures that a buildup of toxic waste does not occur.
- The most significant (and used) product of cellular respiration is energy, which is the fuel for the functioning of our body.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
