Unknown Story
Storyboard Text
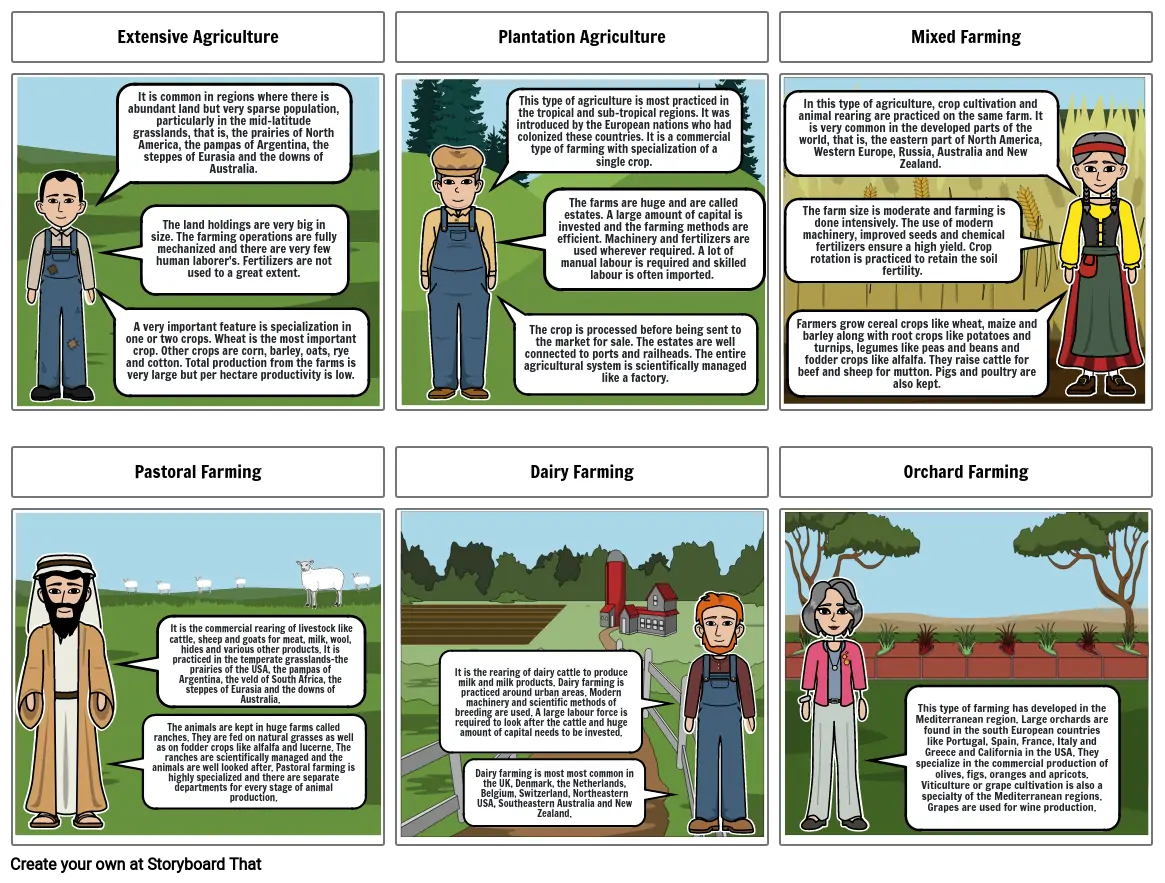
- Extensive Agriculture
- A very important feature is specialization in one or two crops. Wheat is the most important crop. Other crops are corn, barley, oats, rye and cotton. Total production from the farms is very large but per hectare productivity is low.
- It is common in regions where there is abundant land but very sparse population, particularly in the mid-latitude grasslands, that is, the prairies of North America, the pampas of Argentina, the steppes of Eurasia and the downs of Australia.
- The land holdings are very big in size. The farming operations are fully mechanized and there are very few human laborer's. Fertilizers are not used to a great extent.
- Plantation Agriculture
- This type of agriculture is most practiced in the tropical and sub-tropical regions. It was introduced by the European nations who had colonized these countries. It is a commercial type of farming with specialization of a single crop.
- The farms are huge and are called estates. A large amount of capital is invested and the farming methods are efficient. Machinery and fertilizers are used wherever required. A lot of manual labour is required and skilled labour is often imported.
- The crop is processed before being sent to the market for sale. The estates are well connected to ports and railheads. The entire agricultural system is scientifically managed like a factory.
- Mixed Farming
- In this type of agriculture, crop cultivation and animal rearing are practiced on the same farm. It is very common in the developed parts of the world, that is, the eastern part of North America, Western Europe, Russia, Australia and New Zealand.
- Farmers grow cereal crops like wheat, maize and barley along with root crops like potatoes and turnips, legumes like peas and beans and fodder crops like alfalfa. They raise cattle for beef and sheep for mutton. Pigs and poultry are also kept.
- The farm size is moderate and farming is done intensively. The use of modern machinery, improved seeds and chemical fertilizers ensure a high yield. Crop rotation is practiced to retain the soil fertility.
- Pastoral Farming
- It is the commercial rearing of livestock like cattle, sheep and goats for meat, milk, wool, hides and various other products. It is practiced in the temperate grasslands-the prairies of the USA, the pampas of Argentina, the veld of South Africa, the steppes of Eurasia and the downs of Australia.
- Dairy Farming
- It is the rearing of dairy cattle to produce milk and milk products. Dairy farming is practiced around urban areas. Modern machinery and scientific methods of breeding are used. A large labour force is required to look after the cattle and huge amount of capital needs to be invested.
- Orchard Farming
- This type of farming has developed in the Mediterranean region. Large orchards are found in the south European countries like Portugal, Spain, France, Italy and Greece and California in the USA. They specialize in the commercial production of olives, figs, oranges and apricots. Viticulture or grape cultivation is also a specialty of the Mediterranean regions. Grapes are used for wine production.
- The animals are kept in huge farms called ranches. They are fed on natural grasses as well as on fodder crops like alfalfa and lucerne. The ranches are scientifically managed and the animals are well looked after. Pastoral farming is highly specialized and there are separate departments for every stage of animal production.
- Dairy farming is most most common in the UK, Denmark, the Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Northeastern USA, Southeastern Australia and New Zealand.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
