Herzberg's Motivation-Hygiene Theory Continued
Storyboard Description
Part 2
Storyboard Text
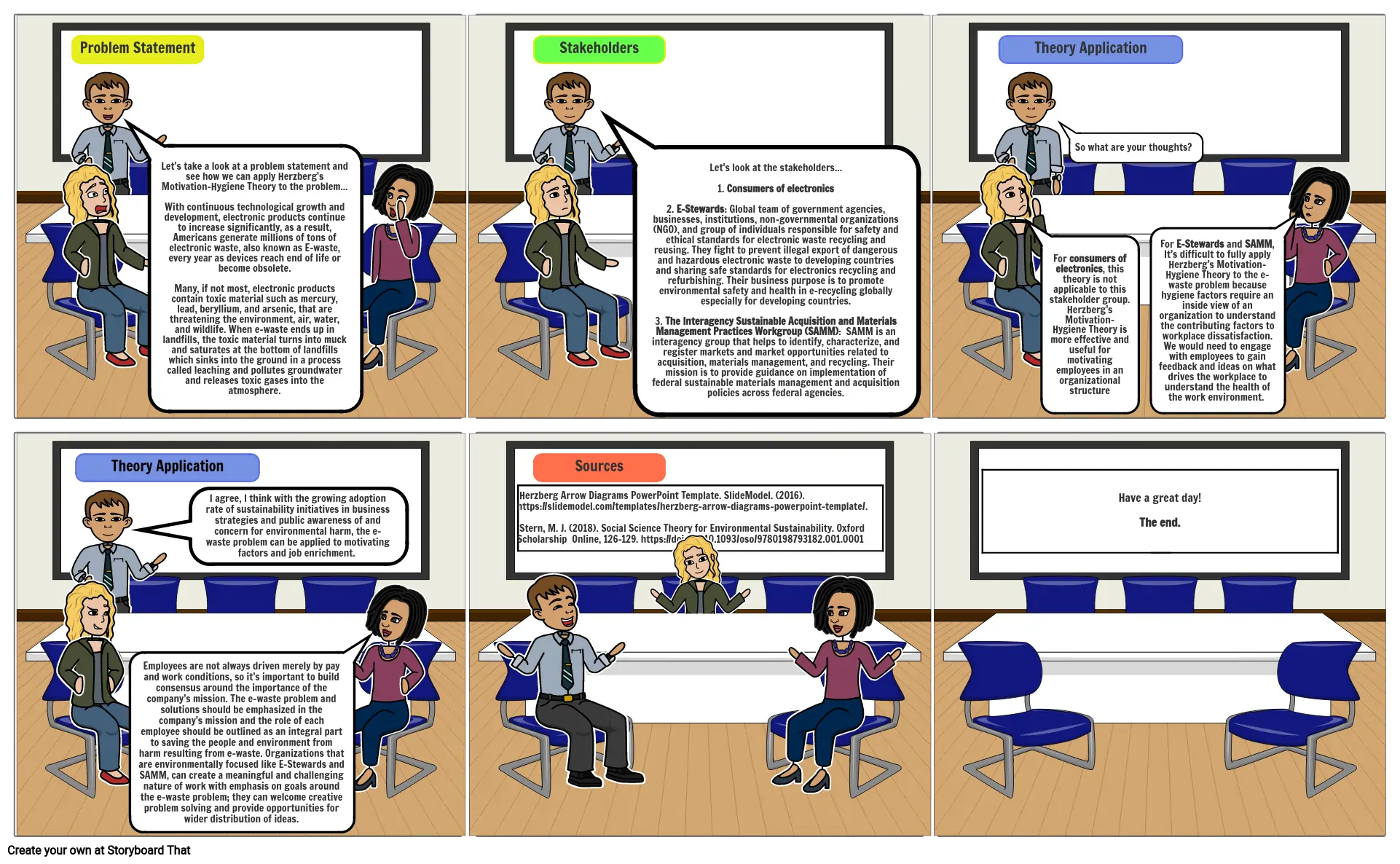
- Problem Statement
- Let's take a look at a problem statement and see how we can apply Herzberg's Motivation-Hygiene Theory to the problem...With continuous technological growth and development, electronic products continue to increase significantly, as a result, Americans generate millions of tons of electronic waste, also known as E-waste, every year as devices reach end of life or become obsolete.Many, if not most, electronic products contain toxic material such as mercury, lead, beryllium, and arsenic, that are threatening the environment, air, water, and wildlife. When e-waste ends up in landfills, the toxic material turns into muck and saturates at the bottom of landfills which sinks into the ground in a process called leaching and pollutes groundwater and releases toxic gases into the atmosphere.
- Stakeholders
- Let's look at the stakeholders...1. Consumers of electronics2. E-Stewards: Global team of government agencies, businesses, institutions, non-governmental organizations (NGO), and group of individuals responsible for safety and ethical standards for electronic waste recycling and reusing. They fight to prevent illegal export of dangerous and hazardous electronic waste to developing countries and sharing safe standards for electronics recycling and refurbishing. Their business purpose is to promote environmental safety and health in e-recycling globally especially for developing countries.3. The Interagency Sustainable Acquisition and Materials Management Practices Workgroup (SAMM): SAMM is an interagency group that helps to identify, characterize, and register markets and market opportunities related to acquisition, materials management, and recycling. Their mission is to provide guidance on implementation of federal sustainable materials management and acquisition policies across federal agencies.
- Theory Application
- For consumers of electronics, this theory is not applicable to this stakeholder group. Herzberg’s Motivation–Hygiene Theory is more effective and useful for motivating employees in an organizational structure
- So what are your thoughts?
- For E-Stewards and SAMM, It’s difficult to fully apply Herzberg’s Motivation–Hygiene Theory to the e-waste problem because hygiene factors require an inside view of an organization to understand the contributing factors to workplace dissatisfaction. We would need to engage with employees to gain feedback and ideas on what drives the workplace to understand the health of the work environment.
- Theory Application
- Employees are not always driven merely by pay and work conditions, so it’s important to build consensus around the importance of the company’s mission. The e-waste problem and solutions should be emphasized in the company’s mission and the role of each employee should be outlined as an integral part to saving the people and environment from harm resulting from e-waste. Organizations that are environmentally focused like E-Stewards and SAMM, can create a meaningful and challenging nature of work with emphasis on goals around the e-waste problem; they can welcome creative problem solving and provide opportunities for wider distribution of ideas.
- I agree, I think with the growing adoption rate of sustainability initiatives in business strategies and public awareness of and concern for environmental harm, the e-waste problem can be applied to motivating factors and job enrichment.
- Herzberg Arrow Diagrams PowerPoint Template. SlideModel. (2016). https://slidemodel.com/templates/herzberg-arrow-diagrams-powerpoint-template/. Stern, M. J. (2018). Social Science Theory for Environmental Sustainability. Oxford Scholarship Online, 126–129. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780198793182.001.0001
- Sources
- Have a great day!The end.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
