challenge 4
Storyboard Text
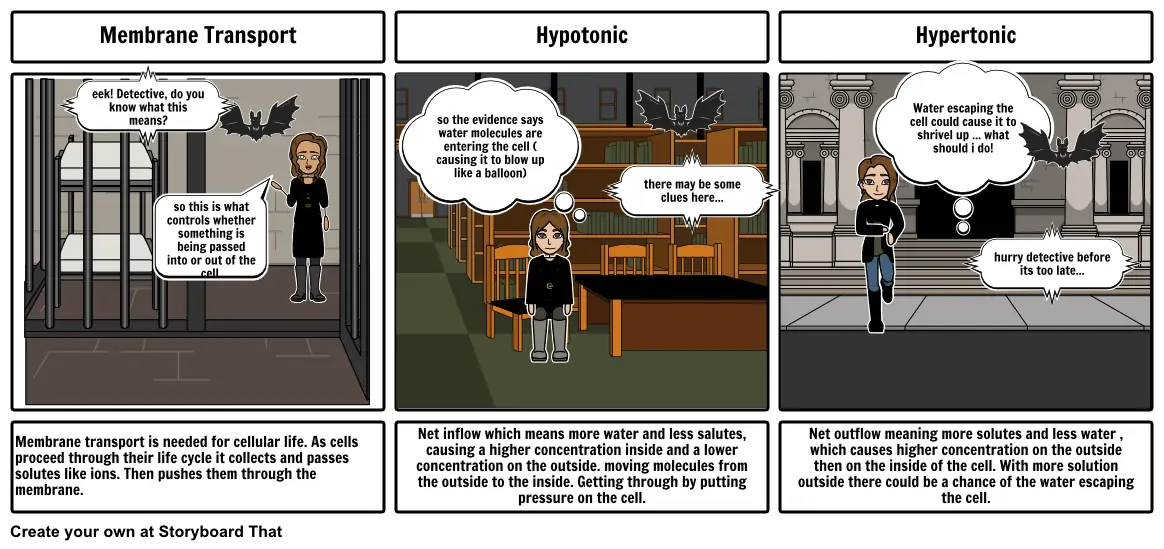
- Membrane Transport
- eek! Detective, do you know what this means?
- so this is what controls whether something is being passed into or out of the cell.
- Hypotonic
- so the evidence says water molecules are entering the cell ( causing it to blow up like a balloon)
- there may be some clues here...
- Hypertonic
- Water escaping the cell could cause it to shrivel up ... what should i do!
- hurry detective before its too late...
- Membrane transport is needed for cellular life. As cells proceed through their life cycle it collects and passes solutes like ions. Then pushes them through the membrane.
- Net inflow which means more water and less salutes, causing a higher concentration inside and a lower concentration on the outside. moving molecules from the outside to the inside. Getting through by putting pressure on the cell.
- Net outflow meaning more solutes and less water , which causes higher concentration on the outside then on the inside of the cell. With more solution outside there could be a chance of the water escaping the cell.
Over 30 Million Storyboards Created
No Downloads, No Credit Card, and No Login Needed to Try!
